Sarah Jane Tribble: Trump has acted to kill Digital Equity Act
From Kaiser Family Foundation Health News, except for images above
“The Internet provides this extra layer of resilience.”
— Christina Filipovic, who leads the research for an initiative of the Institute for Business in the Global Context at Tufts University, in Medford, Mass.
Megan Waiters can recite the stories of dozens of people she has helped connect to the Internet in western Alabama. A 7-year-old who couldn’t do classwork online without a tablet, and the 91-year-old she taught to check health-care portals on a smartphone.
Dead Zone
Millions of rural Americans live in counties with doctor shortages and where high-speed Internet connections aren’t adequate to access advanced telehealth services.
A KFF Health News analysis found people in these “dead zones” live sicker and die younger on average than their peers in well-connected regions.
“They have health-care needs, but they don’t have the digital skills,” said Waiters, who is a digital navigator for an Alabama nonprofit. Her work has involved giving away computers and tablets while also teaching classes on how to use the internet for work and personal needs, like banking and health. “It’s like a foreign space.”
Those stories are now bittersweet.
Waiters is part of a network of digital navigators across the country whose work to bring others into the digital world was, at least in part, propped up by a $2.75 billion federal program that abruptly canceled funding this spring. The halt came after President Trump posted on his Truth Social platform that the Digital Equity Act was unconstitutional and pledged “no more woke handouts based on race!”
The act lists exactly whom the money should benefit, including low-income households, older residents, some incarcerated people, rural Americans, veterans, and members of racial or ethnic minority groups.
Politicians, researchers, librarians, and advocates said defunding the program, along with other changes in federal broadband initiatives, jeopardizes efforts to help rural and underserved residents participate in the modern economy and lead healthier lives.
“You could see lives change,” said Sam Helmick, president of the American Library Association, recalling how they helped grandpas in Iowa check prescriptions online or laid-off factory workers fill out job applications.
The Digital Equity Act is part of the sweeping 2021 infrastructure law, which included $65 billion to build high-speed Internet infrastructure and connect millions without access to the internet.
This year, Congress once again pushed for a modern approach to help Americans, mandating that state leaders prioritize new and emerging technologies through its $50 billion Rural Health Transformation Program.
A KFF Health News analysis found that nearly 3 million people in America live in areas with shortages of medical professionals and where modern telehealth services are often inaccessible because of poor internet connections. The analysis found that in about 200 mostly rural counties where dead zones persist, residents live sicker and die earlier on average than people in the rest of the country. Access to high-speed internet is among a host of social factors, like food and safe housing, that help people lead healthier lives.
“The Internet provides this extra layer of resilience,” said Christina Filipovic, who leads the research for an initiative of the Institute for Business in the Global Context at Tufts University. The research group found in 2022 that access to high-speed internet correlated with fewer covid deaths, particularly in metro areas.
During the covid-19 pandemic, federal lawmakers launched a subsidy program paid for by the infrastructure law. That aid, called the Affordable Connectivity Program, aimed to connect more people to their jobs, schools, and doctors. In 2024, Congress did not renew funding for the subsidy program, which had enrolled about 23 million low-income households.
This year, U.S. Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick revamped and delayed the infrastructure law’s construction initiative — known as the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment Program, or BEAD — after announcing plans to reduce regulatory burdens.
More than 40 states and territories have submitted final proposals to extend high-speed Internet to underserved areas under the administration’s new guidelines, according to a Commerce Department dashboard.
In May, the Digital Equity Act’s funding was terminated within days of Trump’s Truth Social post.
While many states in 2022 had received money to plan their programs, the next round of funding, designated for states and agencies to implement the plans, had largely been awarded but not distributed.
Instead, federal regulators — including the National Telecommunications and Information Administration, the federal agency overseeing implementation of the Digital Equity Act — notified recipients that the grants would be terminated. The grants were created and administered with “unconstitutional racial preferences,” according to the letter.
In Phoenix, officials learned in January that the city was slated to get $11.8 million to increase Internet access and teach digital literacy, but they received an email May 20 stating that all grants, “except for grants to Native Entities,” had been terminated.
“It’s a shame,” said Phoenix Mayor Kate Gallego, a Democrat. The money, she said, would have helped 37,000 residents get Internet access.
Georgia’s Democratic leaders in July sent a letter to Lutnick and NTIA’s then-acting administrator, Adam Cassady, urging reinstatement of the money, noting that the federal cut ignores congressional intent and violates public trust.
The act’s creator, Sen. Patty Murray (D-Wash.), said during an online press conference in May that Republican governors in 2024 supported the law and its funding when each state touted completing its required digital equity plans and asked for resources.
“I cannot believe there aren’t Republican governors out there that are going to join with us to fight back on this,” Murray said, adding “the other way is through courts.”
All 50 states developed digital equity plans after months of focus groups, surveys, and public comment periods. NTIA Digital Equity Director Angela Thi Bennett, during an August 2024 interview with KFF Health News, said the “intentional community engagement” by federal and state leaders to deliver broadband to unserved communities was “the greatest demonstration of participatory democracy our country has ever seen.”
Thi Bennett could not be reached for comment on this article. NTIA spokesperson Stephen Yusko said the agency “will not be able to accommodate” a request for an interview with Thi Bennett and did not respond to questions for this article.
Caroline Stratton, a research director at the Benton Institute for Broadband & Society, said the act’s funding allowed states to staff offices; identify existing high-speed Internet programs, including those operating within other state agencies; and create plans to fill the gaps.
“This sent folks out looking,” Stratton said, to see whether agencies in the state were already working on health-improvement plans and to ask whether the broadband work could contribute and “actively help move the needle.”
State grant applications included goals to promote health care access. In Mississippi, the plan consists of the state university and another agency’s health improvement plan, Stratton said.
While states were required to create programs that would help specific covered populations, some states modified the language or added subcategories to include other populations. Colorado’s plan included immigrants and “individuals experiencing homelessness.”
“In every state, there’s a loss,” said Angela Siefer, executive director of the National Digital Inclusion Alliance. The nonprofit, which was awarded nearly $26 million to work with organizations nationwide but did not receive any funds, filed a lawsuit Oct. 7 seeking to force Trump and the administration to distribute the money.
“The digital divide is not over,” Siefer said.
The nonprofit’s grant had been planned to support digital navigators in 11 states and territories, including Waiters. Her employer, the nonprofit Community Service Programs of West Alabama, expected to receive a $1.4 million grant.
In the past two years, Waiters spent hours driving the roads of rural Alabama to reach residents. She has distributed 648 devices — laptops, tablets, and SIM cards — and helped hundreds of clients through 117 two-hour digital skills classes at libraries, senior centers, and workplace development programs in and around Tuscaloosa, Ala.
People of “all races, of all ages, of all financial backgrounds” who did not “fit into our typical minority category” were helped through her work, Waiters said. Trump and his administration should know, she said, “what it actually looks like for the people I serve.”
Sarah Jane Tribble is a KFF reporter: sjtribble@kff.org, @sjtribble
We’re all entangled
“Hassocky Meadow Trail, Ipswich River Wildlife Sanctuary,’’ in spring 2024, in Mary Lang’s show “Entangled,’’ at Kingston Gallery, Boston, through Nov. 2
She says:
“For decades my photographs had offered a feeling of space, often of groundlessness, of vast sky or open water, or at least an expansive horizon. Now, I am drawn to photograph tangled trees, vines, almost impenetrable thickets of growth. Why? What am I looking at? What am I trying to see? Or describe? This exhibition is the beginning of my answer to that question.
“First, these images are an invitation to take in complexity, to not feel claustrophobic when confronted by layers of growth, of living things, of pathless thickets, of entangled vines and branches. They are an invitation to be awed and drawn to more detail than your mind can absorb. In this fraught world, we need to increase our capacity to handle complexity. Secondly, they are a metaphor for entanglement, a term ecologists and climate activists use to describe the complexity of modernity: everything we do, everything that all of us do, everything that the earth does, is completely entangled, interdependent, inseparable. As human beings living in the Anthropocene era, we can’t avoid our complicity in the harm to the planet.’’
John Whipple House, in Ipswich, was built in 1677.
‘Light, hope, and joy’
“Radiant” (encaustic), by Marcia Crumley, in her show, “Finding Joy,’’ at Blue Door Gallery, York, Maine, through Nov. 9.
The gallery says Crumley’s work “captures the emotional and visual beauty of the natural world. This vibrant collection reflects not only her personal journey through painting, but our shared pursuit of light, hope, and joy in uncertain times. Expect a luminous mix of night skies, seascapes, and color-saturated landscapes that celebrate the everyday wonder around us.’’
Sewall’s 1794 map of York
Aaron Mansfield: Of football fandom and physical health
From The Conversation, except for picture above.
NORTH ANDOVER, Mass.
Aaron Mansfield is an assistant professor of sport management at Merrimack College.
He does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Being from Buffalo means getting to eat some of the best wings in the world. It means scraping snow and ice off your car in frigid mornings. And it means making a lifelong vow to the city’s NFL franchise, the Bills – for better or worse, till death do us part.
When I grew up in New York’s second-largest city, my community was bound together by loyalty to a football team that always found new ways to break our hearts.
And yet at the start of each NFL season, we always found reasons to hope – we couldn’t help ourselves.
Coming from this football-crazed culture, I often wondered about the psychology of fandom. This eventually led me to pursue a Ph.D. in sport consumer behavior. As a doctoral student, I was most interested in one question: Is fandom good for us?
I found a huge body of research on the psychological and social effects of fandom, and it certainly made being devoted to a team look good. Fandom builds belonging, helps adults make friends, boosts happiness and even provides a buffer against traumatic life events.
So, fandom is great, right?
As famed football commentator Lee Corso would say: “Not so fast, my friend.”
While fandom appears to be a boon for our mental health, strikingly little research had been conducted on the relationship between fandom and physical health.
So I decided to conduct a series of studies – mainly of people in Western countries – on this topic. I found that being a sports fan can have some drawbacks for physical health, especially among the most committed fans.
Reach for the nachos
Playing sports is healthy. But watching them? Not so much.
Tailgating culture revolves around alcohol. Research shows that college sports fans binge drink at significantly higher rates than nonfans, are more likely to do something they later regretted and are more likely to drive drunk. Meanwhile, watch parties encourage being stationary for hours and mindlessly snacking. And, of course, fandom goes hand in hand with heavily processed foods like wings, nachos, pizza and hot dogs.
One fan told me that when watching games, his relationship with food is “almost Pavlovian”; he craves “decadent” foods the same way he seeks out popcorn at the movies.
Inside the stadium, healthy options have traditionally been scarce and overpriced. A Sports Illustrated writer joked in 1966 that fans leave stadiums and arenas with “the same body chemistry as a jelly doughnut.”
Little seems to have changed since. One Gen Z fan I recently interviewed griped, “You might find one salad with a plain piece of lettuce and a quarter of a tomato.”
Eating away anxiety and pain
The relationship between fandom and physical health isn’t just about guzzling beer, sitting for hours on end or scarfing down hot dogs.
One study analyzed sales from grocery stores. The researchers found that fans consume more calories – and less healthy food – on the day following a loss by their favorite team, a reaction the researchers tied to stress and disappointment.
My colleagues and I found something similar: Fandom induces what’s called “emotional eating.”
Emotions like anger, sadness and disappointment lead to stronger cravings. And this relationship is tied to how your favorite team performs when it matters most. For example, we found that games between rivals and closely contested games yield more pronounced effects. Emotional states generated by the game are also significantly correlated with increased beer sales in the stadium.
High-calorie cultures
In another paper, my co-authors and I found that fans often feel torn between their desire to make healthy choices and their commitment to being a “true fan.”
Every fan base develops its own culture. These unwritten rules vary from team to team, and they aren’t just about wearing a cheesehead hat or waving a Terrible Towel. They also include expectations around drinking, eating and lifestyle.
These health-related norms are shaped by a variety of factors, including the region’s culture, team history and even team sponsorships.
For example, the Cincinnati Bengals partner with Skyline Chili, a regional chain that makes a meat sauce that’s often poured over hot dogs or spaghetti. One Bengals fan I interviewed observed that if you attend a Bengals game, sure, you could eat something else – but a “true fan” eats Skyline.
I have two studies in progress that show how hardcore fans typically align their health behaviors with the health norms of their fan base. This becomes a way to signal their allegiance to the team, improve their standing among fellow fans, and contribute to what makes the fan base distinct in the eyes of its members.
In Buffalo, for example, tailgating often revolves around alcohol – so much so that Bills fans have a reputation for over-the-top drinking rituals.
And in New Orleans, Saints fans often link fandom to Louisiana food traditions. As one fan explained: “People make a bunch of fried food or huge pots of gumbo or étouffée, and eat all day – from hours before the game until hours after.”
New generation of health-conscious fans
The fan experience is shaped by the culture in which it is embedded. Teams actively help shape these cultures, and there’s a business argument to be had for teams to play a bigger role in changing some of these norms.
Gen Z is strikingly health-conscious. They’re also less engaged with traditional fandom.
If stadiums and tailgates continue to revolve around beer and nachos, why would a generation attuned to fitness influencers and “fitspiration” buy in? To reach this market, I think the sports industry will need to promote its professional sports teams in new ways.
Some teams are already doing so. The British soccer team Liverpool has partnered with the exercise equipment company Peloton. Another club, Manchester City, has teamed up with a nonalcoholic beer brand as the official sponsor of its practice uniforms.
And several European soccer clubs have even joined a “Healthy Stadia” movement, revamping in-stadium food options and encouraging fans to walk and bike to the stadium.
For the record, I don’t think the solution is replacing typical fan foods with smoothies and salads. Alienating core consumers is generally not a sound business strategy.
I think it’s reasonable, however, to suggest sports teams might add more healthy options and carefully evaluate the signals they send through sponsorships.
As one fan I recently interviewed said: “The NFL has had half-assed efforts like Play 60” – a campaign encouraging kids to get at least 60 minutes of physical activity per day – “while also making a ton of money from beer, food and, back in the day, cigarette advertisements. How can sports leagues seriously expect people to be healthier if they promote unhealthy behaviors?”
Today’s consumers want to support brands that reflect their values. This is particularly true for Gen Zers, many of whom are savvy enough to see through hollow campaigns and quick to reject hypocrisy. In the long run, I think this type of dissonance – sandwiching a Play 60 commercial between ads for Uber Eats and Anheuser-Busch – will prove counterproductive.
I, as much as anyone else, understand what makes fandom special – and yes, I’ve eaten my share of wings during Bills games. But public health is a pressing concern, and though the sports industry is well-positioned to address this issue, fandom isn’t helping. Actually, my research suggests it’s having the opposite effect.
Striking the balance I’m advocating will be tricky, but the sports industry is filled with bright problem-solvers. In the film “Moneyball,” Brad Pitt’s character, Billy Beane, famously says sports teams must “adapt or die.” He was referring to the need for baseball teams to integrate analytics into their decision-making.
Professional sports teams eventually got that message. Maybe they’ll get this one, too.
‘Why so soon’
“Autumn in The Berkshires” (circa 1919), by Christian Jorgensen.
Ere, in the northern gale,
The summer tresses of the trees are gone,
The woods of Autumn, all around our vale,
Have put their glory on.
The mountains that infold,
In their wide sweep, the coloured landscape round,
Seem groups of giant kings, in purple and gold,
That guard the enchanted ground.
I roam the woods that crown
The upland, where the mingled splendours glow,
Where the gay company of trees look down
On the green fields below.
My steps are not alone
In these bright walks; the sweet south-west, at play,
Flies, rustling, where the painted leaves are strown
Along the winding way.
And far in heaven, the while,
The sun, that sends that gale to wander here,
Pours out on the fair earth his quiet smile,--
The sweetest of the year.
Where now the solemn shade,
Verdure and gloom where many branches meet;
So grateful, when the noon of summer made
The valleys sick with heat?
Let in through all the trees
Come the strange rays; the forest depths are bright?
Their sunny-coloured foliage, in the breeze,
Twinkles, like beams of light.
The rivulet, late unseen,
Where bickering through the shrubs its waters run,
Shines with the image of its golden screen,
And glimmerings of the sun.
But 'neath yon crimson tree,
Lover to listening maid might breathe his flame,
Nor mark, within its roseate canopy,
Her blush of maiden shame.
Oh, Autumn! why so soon
Depart the hues that make thy forests glad;
Thy gentle wind and thy fair sunny noon,
And leave thee wild and sad!
Ah! 'twere a lot too blessed
For ever in thy coloured shades to stray;
Amid the kisses of the soft south-west
To rove and dream for aye;
And leave the vain low strife
That makes men mad--the tug for wealth and power,
The passions and the cares that wither life,
And waste its little hour.
— “Autumn Woods,’’ by William Cullen Bryant (1794-1878), American poet, essayist and editor. He grew up in Cummington, Mass., just east of The Berkshires.
A matter of priorities
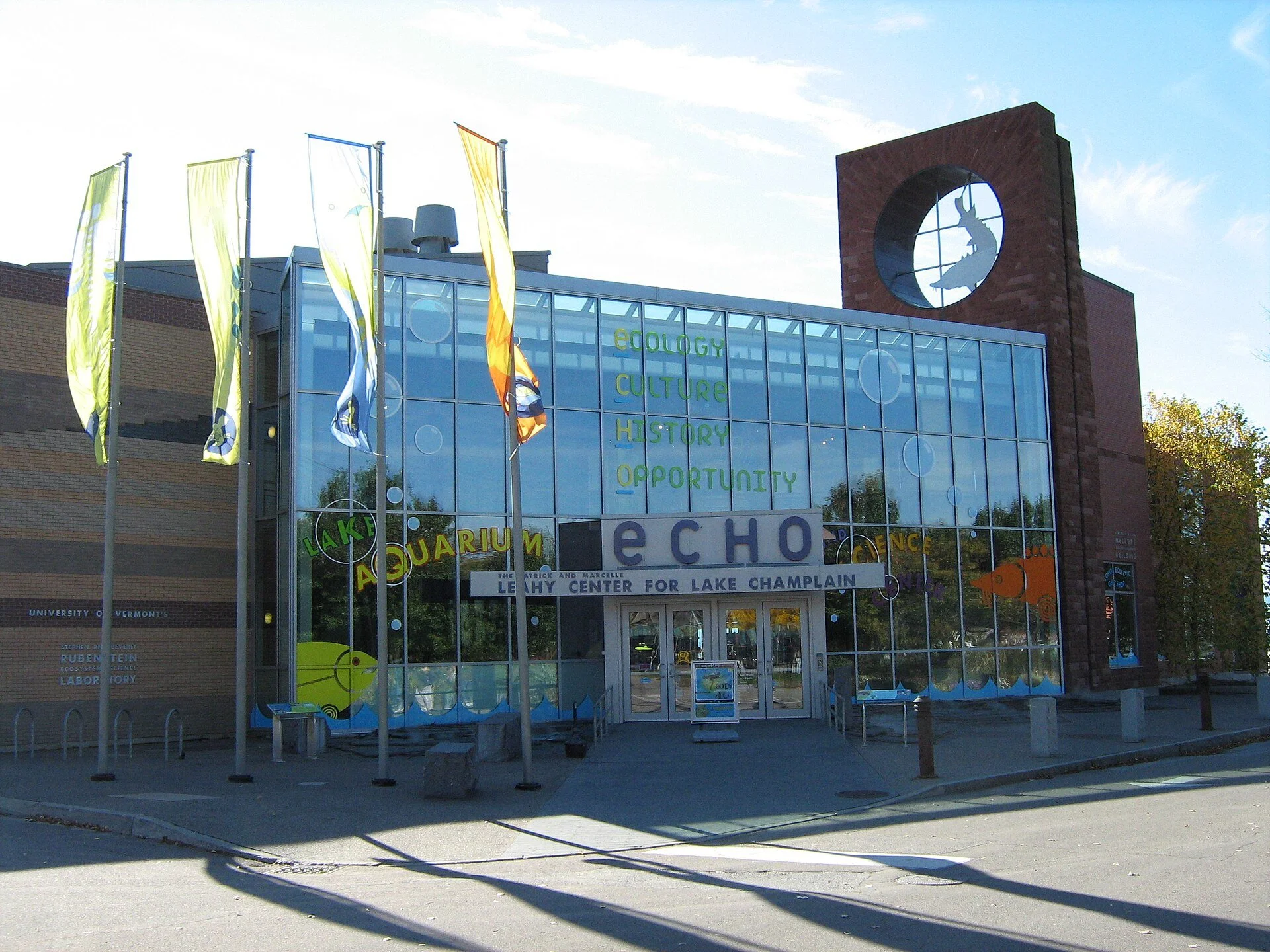
ECHO, Leahy Center for Lake Champlain, in Burlington.
Photo by Mfwills
“If the environment were a bank, it would have been saved by now.’’
— Bernie Sanders, U.S. senator from Vermont and a former mayor of Burlington
Drama queen
“Vaneeta,’’ from the show “Little Dramas,’’ by B. Lynch, at Danforth Art Museum, Framingham, Mass., through Jan. 11.
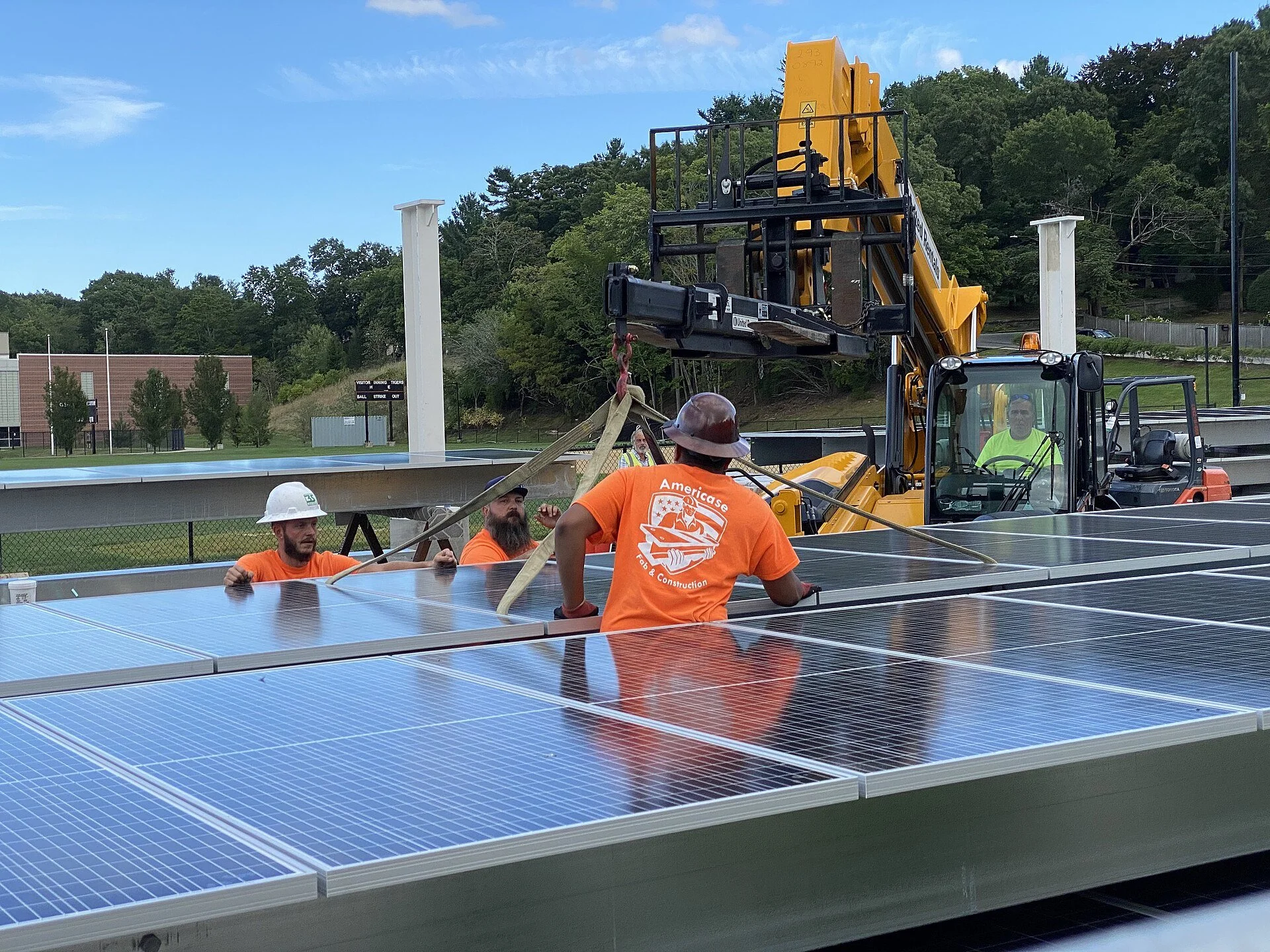
Mass. looks to the sun
In Massachusetts, solar installation at Newton North High School
ArnoldReinhold photo
Sun in the Bay State
Adapted from Robert Whitcomb’s “Digital Diary,’’ in GoLocal24.com
Massachusetts Gov. Maura Healey is quite right to say that generating much more solar energy, and storing it with improved batteries, is the fastest and most efficient way to address the state’s increasing energy needs. That’s especially given such gargantuan electricity consumers as more data centers, especially for artificial intelligence, come online.
Indeed, local-and-state-overseen solar energy not vulnerable to shifting federal policies/politics is becoming ever more needed in the state. That’s partly because Washington’s current rulers dislike any energy not produced by burning oil, gas and coal. (The fossil-fuel folks, based in Red States, are big Republican campaign donors.) And Trump particularly hates offshore wind projects, which he has been halting despite the billions of dollars that have been spent on them so far. Massachusetts officials had hoped that those turbines would meet much of the state’s electricity needs in the next few years.
So Ms. Healey’s administration has filed emergency regulations for the Solar Massachusetts Renewable Target (SMART) program to try to lower installation costs, speed up permitting and expand interconnections for solar.
The governor noted:
“Solar energy in Massachusetts, on the hottest single day of summer this year — behind-the-meter solar, which is the solar on our roofs and farms and schools — met 22 percent of statewide demand.’’ Data indicate that solar accounted for almost 27 percent of the state's electricity supply as of late 2024, up from 19 percent in 2020. It’s a very good thing it’s rising so fast: ISO New England, the region’s grid operator, predicts that power demand in New England will rise 11 percent by 2034.
But there can be big siting issues for solar farms, as opposed to rooftop installations. Cutting down trees should be avoided! Trees, by absorbing CO2 produced by fossil-fuel burning, obviously slow global warming.
Vacant developed land (such as parking areas of dead stores and malls) and roadside and median strips are good places for solar. If such facilities must be put in countryside fields, then grow plants below them. The plants of course absorb carbon dioxide. In a few farms, goats and sheep graze below high-mount solar-panel platforms. Farmers get some added revenue from selling the power to utilities.
Time is of the essence. Federal tax credits for nonresidential renewable-energy projects will expire at the end of 2027, and residential tax credits for renewable energy (which includes wind turbines but mostly involves rooftop solar) will shut off at the end of this year.
Much of the rest of the world is moving to renewable energy considerably faster than America as “green energy’’ installation cost declines and worry about global warming and pollution rises.
Big Oct. 23 event at the Newport Art Museum
“On the Veranda (The Blue Porch)’’ (1909 oil on canvas), by Howard Gardiner Cushing, in the show “Howard Gardiner Cushing: A Harmony of Line and Color,’’ through Dec. 31, at the Newport Art Museum. See this event.
Exploring presence and absence
“Grace Looking Through Hole in Log” (archival pigment print), by Scott Offen, in the show “Grace by Scott Offen,’’ at Panopticon Gallery, Boston, through Dec. 2.
The gallery says:
“The show, coinciding with the launch of Offen’s monograph with L’Artiere Edizioni, the exhibition features intimate, dreamlike portraits performed and co-created by his wife, Grace. Exploring collaboration, identity, and connection with nature, the work invites reflection on presence and absence.’’
Llewellyn King: AI could be apocalyptic for jobs
WEST WARWICK, R.I.
The Big One is coming, and it isn't an earthquake in California or a hurricane in the Atlantic. It is the imminent upending of so many of the world's norms by artificial intelligence, for good and for ill.
Jobs are being swept away by AI not in the distant future, but right now. A recent Stanford University study found that entry-level jobs for workers between 22 and 25 years old have dropped by 13 percent since the widespread adoption of AI.
Another negative impact of AI: The data centers that support AI are replacing farmland at a rapid rate. The world is being overrun with huge concrete boxes, Brutalist in their size and visual impact.
Meta Platforms (of which Facebook is part) plans to spend hundreds of billions of dollars to build several massive AI data centers; the first called Prometheus and the second Hyperion.
CEO Mark Zuckerberg said in a post on his Threads social media platform: “We're building multiple more titan clusters as well. Just one of these covers a significant part of the footprint of Manhattan.”
Data centers are voracious in their consumption of electricity and are blamed for sending power bills soaring across the country.
But AI has had a positive impact on the quality of medicine, improving accuracy, consistency and efficacy, according to the National Institutes of Health.
Predictive medicine is on a roll: Alzheimer's Disease and some cancers, for example, can be predicted accurately. That raises the question: Do you want to know when you will lose your mind or get cancer?
Where AI is without downside is medical “exaptation.” That happens when a drug or therapy developed for one disease is found to be effective with another, opening up a field of possibilities.
AI also offers the chance of shortening clinical trials for new drugs from years to a few months. Side effects and downsides can be mapped instantly.
Life expectancy is predicted to increase substantially because of AI. Omar Hatamleh, an AI expert and author, told me, “A child born today can expect to live to 120.”
Likewise, predictive maintenance with AI is already useful in forecasting the failure of industrial plants, power station components and bridges.
Oh, and productivity will increase across the board where AI and AI agents — the AI tools developed for special purposes — are at work.
The trouble is AI will be doing the work that heretofore people have done.
Pick a field and speculate on the job losses there. This may be fun to do as a parlor game, but it is deeply distressing when you realize that it could happen in the very near future — such as in the next year.
Most are low-skilled white-collar jobs, such as those in call centers, or in medical offices checking insurance claims, or in an accounting firm doing bookkeeping. In short, if you are a paper pusher, you will be pushed out.
Look a little further — maybe 10 years — and Uber, which has invested heavily in autonomous vehicles, will have decided that they are ready for general deployment. Bye-bye Uber driver, hello driverless car.
Taxis and truck drivers might well be the next to get to their career-end destinations quicker than they expected.
By the way, autonomous vehicles ought to have fewer accidents than cars with drivers do, so the insurance industry will take a hit and lots of workers there will get the heave-ho. And collision repairs may be nearly outdated.
These aren't speculation; they are real possibilities in the near future. Yet the political world has been arguing about other things.
As far as I am aware, when the leadership of the U.S. military gathered at the Marine Corp Base Quantico in Virginia on Sept. 30 to get a pep talk on shaving, losing weight and gender superiority, they didn't hear about how AI is transforming war and what measures should be taken. Or whether there will be work for those who leave the military.
The Big One is coming, and the politicians are worrying about yesterday's issues. That is like worrying about your next guest list when an uninvited guest, a tsunami of historic proportions, is coming ashore.
On X: @llewellynking2
Bluesky: @llewellynking.bsky.social
Llewellyn King is executive producer and host of White House Chronicle, on PBS. He’s based in Rhode Island.
Brandeis will revamp its curriculum
The rather bizarre Usen Castle, at Brandeis University, in Waltham, Mass.
Edited from a New England Council report
Brandeis University will revamp its curriculum to center it around career-readiness. The university’s president, Arthur Levine, recently introduced ‘‘The Brandeis Plan for Reinventing the Liberal Arts,’’ which aims to give students new skills and the opportunity to enter the workforce early.
The new plan’s key elements include a redesigned core curriculum, a focus on career development from day one of a student’s time at Brandeis, a career-competency second transcript, and a unified academic structure that combines liberal arts with professional education.
‘‘We’re choosing a bold path forward, one that invests in Brandeis’s academic future and reaffirms our leadership in higher education,’’ said Lisa Kranc, chairwoman of the Brandeis Board of Trustees.
Or just realism
“Apathy” (plastic, wire, wood, PVC pipe, cement block), in Sally B. Moore’s show “Human/Beast” at Boston Sculptors Gallery, through Nov. 2
Chris Powell: Enough with Conn. basketball!
Connecticut Sun logo
MANCHESTER, Conn.
Why are Connecticut Gov, Ned Lamont and state Treasurer Erick Russell so enthusiastic about using state pension money to make state government a minority owner of the Mohegan tribe's Connecticut Sun women's basketball team and move it to Hartford from the tribe's reservation in rural eastern Connecticut?
Though questions abound, the governor and the treasurer don't seem to have conducted even a basic analysis of the team's current and likely future finances.
On the Mohegan reservation the Sun plays for free at the tribe's beautiful arena. Do the governor and treasurer suppose that the team also could play for free at the People's Bank Arena, in Hartford, which is overseen by the Capital Regional Development Authority? Has the authority been asked if it would forego revenue and incur only expenses from a major new tenant?
Playing in Hartford, the Sun would face intense competition from the University of Connecticut men's and women's basketball teams, which play most of their games at the People's Bank Arena, not on campus in rural Storrs. Such competition almost certainly would impair the profitability of all three teams. Have the governor and treasurer factored this into whatever informal calculations they have made?
For eight years Hartford has had a beautiful minor-league baseball stadium downtown. Yet the stadium is still making only financial losses for the city, and the city is heavily subsidized by state government. Does state government want to subsidize the city indefinitely for another big entertainment project?
The Hartford office-building project called Constitution Plaza was built in the early 1960s in the hope of reviving downtown and the city generally. It didn't. Today Constitution Plaza is sleepy.
The same aspiration was behind the predecessor of the People's Bank Arena, the Hartford Civic Center, which opened in 1975. The civic center came with a shopping mall. But Hartford continued its decline demographically and economically anyway, and with few customers the shopping mall went out of business.
Twenty years ago state government decided to push downtown Hartford around for the third time in 40 years with the Adriaen's Landing project -- a convention hall, hotel, museum, and restaurant district. But it too is sleepy and has yet to do much for the city.
Indeed, a decade ago the Hartford area's shopping, restaurant, and entertainment focus shifted to West Hartford because of the better demographics there and the greater amount of housing nearby.
The arena in downtown Hartford has served a great purpose for Connecticut, in large part because the UConn teams have played there so often, much closer to the state's center of population than Gampel Pavilion.
But does anyone really believe that the big problem of the Hartford area is the lack of a professional women's basketball team when there is already so much great basketball and some good minor-league baseball in the city?
A century ago Hartford was believed to be the richest city in the country. Today it is among the poorest. Why it changed is yet to be examined officially, but all the games played at the downtown arena and the baseball stadium haven't yet persuaded middle-class people to return to the city to live. Most people at the games go home to the suburbs.
Only more middle-class housing and middle-class schools are likely to restore the city -- schools with academic tests for admission and advancement, not schools like Hartford's, which happily advance and graduate illiterates without apology. All other undertakings in the name of reviving Hartford are mere distractions.
With luck the Women's National Basketball Association will disabuse the governor, the treasurer, and state legislators out of using pension money to become a powerless minority owner -- a prisoner -- of an undertaking that risks becoming a long-term loss. The league and the Mohegans know that Connecticut is a much smaller market than Boston and Houston and a team in those cities would be much more profitable. The league and the Mohegans want only to make money, which is fine, especially since state government often seems to want only to lose it.
Chris Powell has written about Connecticut government and politics for many years (CPowell@cox.net).
The circle route
“Topography No.2’’ (acrylic on canvas) by Christopher O’Connor, at Portland (Maine) Art Gallery.
‘Even toward dark’
Archibald MacLeish in 1944.
“We are as great as our belief in human liberty—no greater. And our belief in human liberty is only ours when it is larger than ourselves: liberty, as Mr. Lincoln put it, ‘not alone to the people of this country but hope to the world.’ We must become again his ‘last, best hope of earth’ if we wish to be the great Republic which his love once saved. We know that we must say so even now, even toward dark, without voice to lead us, without a leader standing to come forth. We must say it for ourselves. No one else will say it for us
Archibald MacLeish (1892-1982), poet, playwright, essayist, government official and lawyer. He lived much of his adult life in Conway, Mass. This was in a column he wrote for The New York Times of July 3, 1976. He referenced the Watergate scandal.
Very good and very bad
Henry Ward Beecher
“Perhaps nowhere in the world can be found more unlovely wickedness — a malignant, bitter, tenacious hatred of good — than in New England. The good are very good and the bad are very bad.’’
Henry Ward Beecher (1813-1887), Congregational minister, reformer and writer in his 1868 novel, Norwood, or Village Life in New England. His adultery trial transfixed the nation.
Monica Duffy Toft: Eisenhower wouldn’t have agreed with bombastic Hegseth
President Eisenhower delivering his televised farewell address on Jan. 17, 1961.
From The Conversation, except for picture above.
Monica Duffy Toft is professor of international politics and director of the Center for Strategic Studies at The Fletcher School, Tufts University.’
She does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
MEDFORD, Mass.
Hundreds of generals and admirals converged on Quantico, Va., on Sept. 30, 2025, after being summoned from across the globe by their boss, Pentagon chief Pete Hegseth, for a session that, as expected, covered what Hegseth often describes as the “warrior ethos.”
Listening quietly, they heard Hegseth promise to make the military “stronger, tougher, faster, fiercer and more powerful than it has ever been before,” and declare that he would fix “decades of decay” in the military.
President Donald Trump spoke for more than an hour in a political speech that derided presidents who came before him. He asserted that “political correctness” would be banished from the military.
The meeting came soon after Trump’s Sept. 5 executive order renaming the Department of Defense the “Department of War.” With that change, Trump reverted the department to a name not used since the 1940s.
The change represents far more than rebranding. It signals an escalation in the administration’s embrace of a militaristic mindset that, in 1961, President Dwight D. Eisenhower warned against in his farewell address, and that the nation’s founders deliberately aimed to constrain.
The timing of this name change feels particularly notable when considered alongside recent reporting revealing secret U.S. military operations. In 2019, a detachment of U.S. Navy SEALs crept ashore in North Korea on a mission to plant a listening device during high-stakes nuclear talks. The risks were enormous: Discovery could have sparked a hostage crisis or even war with a nuclear-armed foe.
That such an operation was approved by Trump in his first term at all exemplifies an increasingly reckless militarism that has defined American foreign policy for decades. That militarism is the very subject of my book, “Dying by the Sword.”
Further, the name change was announced just days after Trump authorized a U.S. military strike on a Venezuelan boat that the administration claimed was carrying drug-laden cargo and linked to the Tren de Aragua cartel. The strike killed 11 people. The administration justified the killings by labeling them “narcoterrorists.”
The U.S. has beefed up military exercises in Puerto Rico during a campaign in the Southern Caribbean against boats suspected of transporting illegal drugs. Miguel J. Rodríguez Carrillo/Getty Images
Abandoning restraint
The Department of War existed from 1789 until 1947, when Congress passed the National Security Act reorganizing the armed services into the National Military Establishment. Just two years later, lawmakers amended the act, renaming the institution the Department of Defense.
Officials disliked the “NME” acronym – which sounded uncomfortably like “enemy” – but the change was not only about appearances.
In the aftermath of World War II, U.S. leaders wanted to emphasize a defensive rather than aggressive military posture as they entered the Cold War, a decades-long standoff between the United States and Soviet Union defined by a nuclear arms race, ideological rivalry and proxy wars short of direct great-power conflict.
The new emphasis also dovetailed with the new U.S. grand strategy in foreign affairs – diplomat George F. Kennan’s containment strategy, which aimed to prevent the expansion of Soviet power and communist ideology around the world.
Kennan’s approach narrowly survived a push to a more aggressive “rollback” strategy of the Soviet Union from its occupation and oppression of central and eastern Europe. It evolved instead into a long game: a team effort to keep the adversary from expanding to enslave other peoples, leading to the adversary’s collapse and disintegration without risking World War III.
On the ground, this meant fewer preparations for war and more emphasis on allies and intelligence, and foreign aid and trade, along with the projection of defensive strength. The hope was that shaping the environment rather than launching attacks would cause Moscow’s influence to wither. To make this strategy viable, the U.S. military itself had to be reorganized.
In a 1949 address before Congress, President Harry S. Truman described the reorganization sparked by the 1947 legislation as a “unification” of the armed forces that would bring efficiency and coordination.
But a deeper purpose was philosophical: to project America’s military power as defensive and protective, and for Truman, strengthening civilian oversight.
The wisdom of this restraint is clearest in Eisenhower’s farewell address, of January 1961.
In less than 10 minutes, the five-star general who had commanded Allied forces in Europe as they swept to victory in World War II cautioned Americans against the rise of a “military-industrial complex.” He acknowledged that the nation’s “arms must be mighty, ready for instant action,” but warned that “the potential for the disastrous rise of misplaced power exists and will persist.”
New enemies, destabilizing regions
The risky North Korean team mission by the Navy SEALs illustrates how America’s militaristic approach often produces the very dangers it aspires to deter.
Rather than enhancing diplomacy, the operation risked derailing talks and escalating conflict. This is the central argument of my book: America’s now-reflexive reliance on armed force doesn’t make America great again or more secure. It makes the country less secure, by creating new enemies, destabilizing regions and diverting resources from the true foundations of security.
It also makes the U.S less admired and respected. The State Department budget continues to be dwarfed by the Department of War’s budget, with the former never reaching more than 5.5% of the latter. And the U.S. Agency for International Development, or USAID, once the leading arm of U.S. soft power as quiet purveyor development aid around the world, is now shuttered.
Today’s Pentagon budget exceeds anything Eisenhower could have imagined.
Trump’s rebranding of the Department of Defense into the Department of War signals a shift toward framing U.S. power primarily in terms of military force. Such a framing emphasizes the use of violence as the principal means of solving problems and equates hostility and aggression with leadership.
Yet historical experience shows that military dominance alone has not translated into strategic success. That’s the mindset that lost the U.S. endless wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, and failed in interventions in Libya and Syria – conflicts that altogether cost trillions of dollars and hundreds of thousands of lives while leaving the country less secure and eroding its international legitimacy.
“Only an alert and knowledgeable citizenry,” Eisenhower said, can compel the proper balance between military power and peaceful goals.
The very title of my and my co-author’s book comes from the Gospel of Matthew – Chapter 26, verse 52 – that “to live by the sword is to die by the sword.”
Throughout modern history, true security has come from diplomacy, international law, economic development and investments in health care and education. Not from an imaginary “warrior ethos.”
America, I would argue, doesn’t need a Department of War. It needs leaders who understand, as Eisenhower did, that living by the sword will doom us all in the end. Real security comes from the quiet power that builds legitimacy and lasting peace. The U.S. can choose again to embody those strengths, to lead not by fear but by example.
At new museum in Westerly
“Autumnal Landscape,’’ by Harriet Randall Lumis (1870-1953), at the new Westerly (R.I.) Museum of American Impressionism.