Vox clamantis in deserto
Rachel Bluth: Noise pollution jangles nerves and hurts sleep
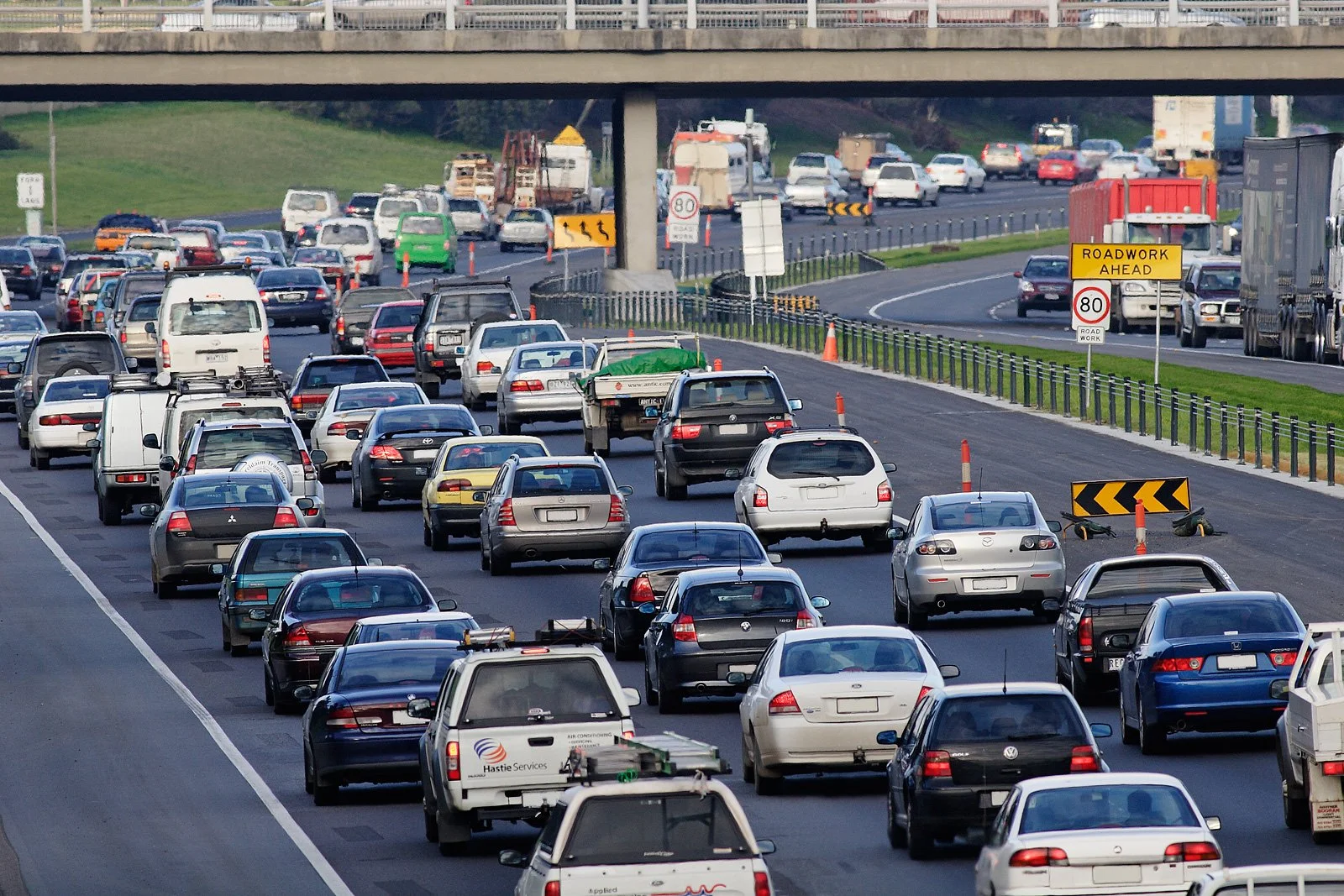
Measuring the noise from a leaf blower.
— Photo by fir0002
When there’s a loud noise, the auditory system signals that something is wrong, triggering a fight-or-flight response in the body and flooding it with stress hormones that cause inflammation and can ultimately lead to disease.
— Peter James, an assistant professor of environmental health at Harvard University’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
SACRAMENTO
Mike Thomson’s friends refuse to stay over at his house anymore.
Thomson lives about 50 yards from a busy freeway that bisects California’s capital city, one that has been increasingly used as a speedway for high-speed races, diesel-spewing big rigs, revving motorcycles — and cars that have been illegally modified to make even more noise.
About the only time it quiets down is Saturday night between 3 and 4 a.m., Thomson said.
Otherwise, the din is nearly constant, and most nights, he’s jolted out of sleep five or six times.
“Cars come by and they don’t have mufflers,” said Thomson, 54, who remodels homes for a living. “It’s terrible. I don’t recommend it for anyone.”
Thomson is a victim of noise pollution, which health experts warn is a growing problem that is not confined to our ears, but causes stress-related conditions like anxiety, high blood pressure, and insomnia.
California legislators passed two laws in 2022 aimed at quieting the environment. One directs the California Highway Patrol to test noise-detecting cameras, which may eventually issue automatic tickets for cars that make noise above a certain level. The other forces drivers of illegally modified cars to fix them before they can be re-registered.
“There’s an aspect of our society that likes to be loud and proud,” said state Sen. Anthony Portantino (D-Glendale), author of the noise camera law. “But that shouldn’t infringe on someone else’s health in a public space.”
Most states haven’t addressed the assault on our eardrums. Traffic is a major driver of noise pollution — which disproportionately affects disadvantaged communities — and it’s getting harder to escape the sounds of leaf blowers, construction, and other irritants.
California’s laws will take time and have limited effect, but noise control experts called them a good start. Still, they do nothing to address overhead noise pollution from circling police helicopters, buzzing drones, and other sources, which is the purview of the federal government, said Les Blomberg, executive director of the Noise Pollution Clearinghouse.
In October 2021, the American Public Health Association declared noise a public health hazard. Decades of research links noise pollution with not only sleep disruption, but also a host of chronic conditions such as heart disease, cognitive impairment, depression, and anxiety.
“Despite the breadth and seriousness of its health impacts, noise has not been prioritized as a public health problem for decades,” the declaration says. “The magnitude and seriousness of noise as a public health hazard warrant action.”
When there’s a loud noise, the auditory system signals that something is wrong, triggering a fight-or-flight response in the body and flooding it with stress hormones that cause inflammation and can ultimately lead to disease, said Peter James, an assistant professor of environmental health at Harvard University’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Constant exposure to noise increases the risk of heart disease by 8% and diabetes by 6%, research shows. The European Environment Agency estimated in 2020 that noise exposure causes about 12,000 premature deaths and 48,000 cases of heart disease each year in Western Europe.
While California Highway Patrol officials will spend the next few years researching noise cameras, they acknowledge that noise from street racing and so-called sideshows — where people block off intersections or parking lots to burn out tires or do “doughnuts” — has surged over the past several years and disturbs people right now.
Cars in California are supposed to operate at 95 decibels — a little louder than a leaf blower or lawn mower — or less. But drivers often modify their cars and motorcycles to be louder, such as by installing “whistle tips” on the exhaust system to make noise or removing mufflers.
In 2021, the last full year for which data is available, the highway patrol issued 2,641 tickets to drivers for excessive vehicle noise, nearly double 2018’s 1,400 citations.
“There’s always been an issue with noise coming from exhausts, and it’s gained more attention lately,” said Andrew Poyner, a highway patrol captain. “It’s been steadily increasing over the past several years.”
The American Public Health Association says the federal government should regulate noise in the air, on roads, and in workplaces as an environmental hazard, but that task has mostly been abandoned since the federal Office of Noise Abatement and Control was defunded in 1981 under President Ronald Reagan.
Now the task of quieting communities is mostly up to states and cities. In California, reducing noise is often a byproduct of other environmental policy changes. For instance, the state will ban the sale of noisy gas-powered leaf blowers starting in 2024, a policy aimed primarily at reducing smog-causing emissions.
One of the noise laws approved in California in 2022, AB 2496, will require owners of vehicles that have been ticketed for noise to fix the issue before they can re-register them through the Department of Motor Vehicles. Currently, drivers can pay a fine and keep their illegally modified cars as they are. The law takes effect in 2027.
The other law, SB 1097, directs the highway patrol to recommend a brand of noise-detecting cameras to the legislature by 2025. These cameras, already in use in Paris, New York City, and Knoxville, Tenn., would issue automatic tickets if they detected a car rumbling down the street too loudly.
Originally, the law would have created pilot programs to start testing the cameras in six cities, but lawmakers said they wanted to go slower and approved only the study.
Portantino said he’s frustrated by the delay, especially because the streets of Los Angeles have become almost unbearably loud.
“It’s getting worse,” Portantino said. “People tinker with their cars, and street racing continues to be a problem.”
The state is smart to target the loudest noises initially, the cars and motorcycles that bother people the most, Blomberg said.
“You can make every car coming off the line half as loud as it is right now and it would have very little impact if you don’t deal with all the people taking their mufflers off,” he said. “That outweighs everything.”
Traffic noise doesn’t affect everyone equally. In a 2017 paper, James and colleagues found that nighttime noise levels were higher in low-income communities and those with a large proportion of nonwhite residents.
“We’ve made these conscious or subconscious decisions as a society to put minority-race communities and lower-income communities who have the least amount of political power in areas near highways and airports,” James said.
Elaine Jackson, 62, feels that disparity acutely in her neighborhood, a low-income community in northern Sacramento sandwiched between freeways.
On weekends, sideshows and traffic noise keep her awake. Her nerves are jangled, she loses sleep, her dogs panic, and she generally feels unsafe and forgotten, worried that new development in her neighborhood would just bring more traffic, noise, and air pollution.
Police and lawmakers don’t seem to care, she said, even though she and her neighbors constantly raise their concerns with local officials.
“It’s hard for people to get to sleep at night,” Jackson said. “And that’s a quality-of-life issue.”
Rachel Bluth is a Kaiser Health News reporter.
Don’t rush them
Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr. (1809-1894)
"Knowledge and timber shouldn't be used until they are seasoned.’’
— Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr. in The Autocrat of the Breakfast Table. A polymath, he was a pioneering Boston-based physician as well as a poet. His son, OIiver Wendell Holmes Jr. (1841-1935) became a famed member of the U.S. Supreme Court and legal scholar. Like his father, he was famed for his witty and pithy remarks.
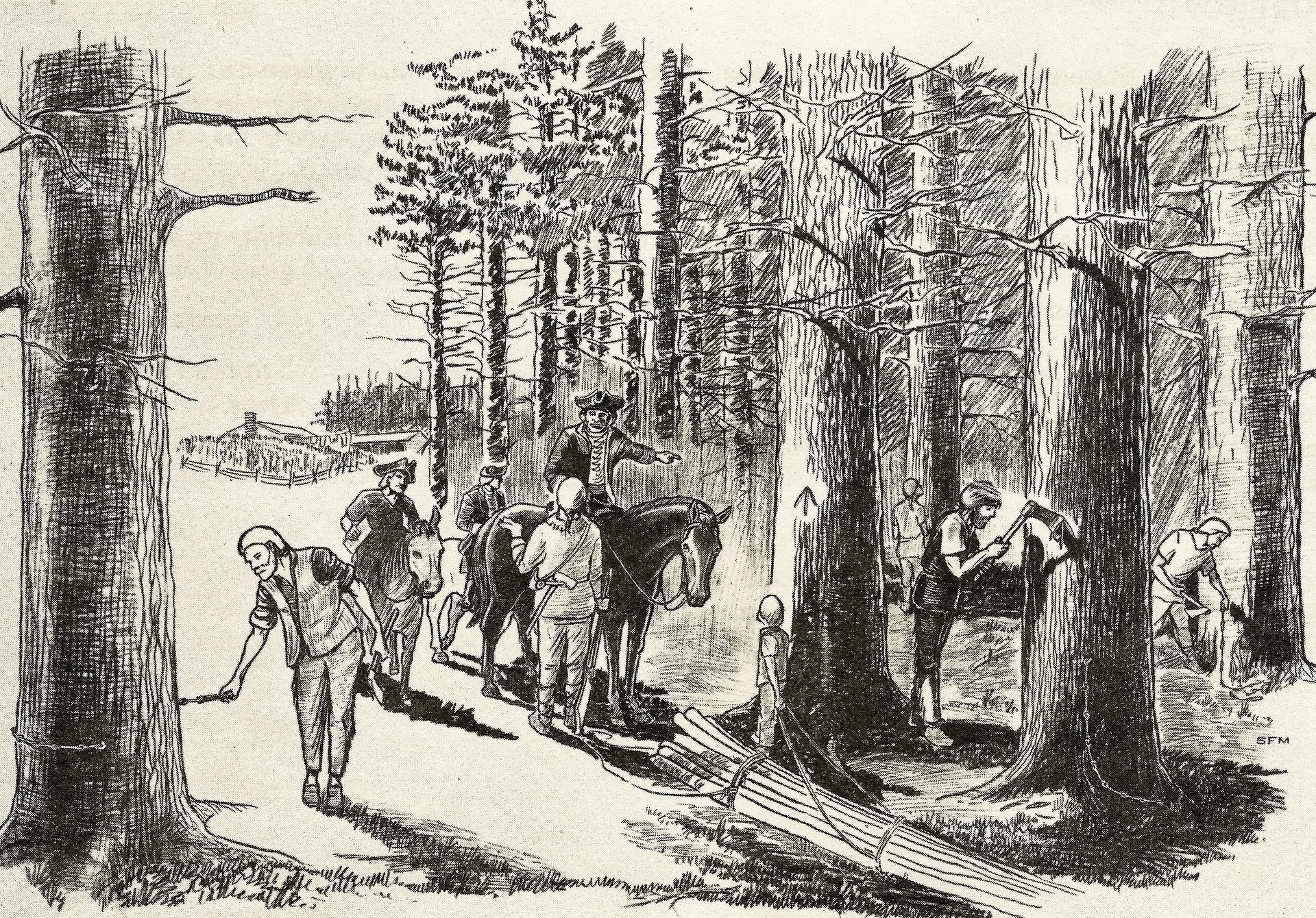
Agents of the king marking New England white pines to be used by the Royal Navy as masts in the 18th Century.
David Warsh: Support Ukraine but study the path to war
"The Chateau" at St. Basil College, in Stamford, Conn., was originally a college dormitory and now houses the Ukrainian Museum and Library of Stamford.
SOMERVILLE, Mass.
I have lived with the possibility of war in Ukraine for a long time, first as a newspaper columnist, then as a newsletter writer (and a long-ago war correspondent). I wrote against further NATO enlargement soon after Poland, Czechoslovakia and Hungary were admitted – gingerly at first, more firmly once I began covering the Harvard-Russia scandal in the mid-’90s.
Boris Yeltsin’s selection of Vladimir Putin to be his successor didn’t seem surprising. Unlike Hillary Clinton, I was not shocked when, in 2012, Putin took back the helm from Dimitri Medvedev. Putin wasn’t a czar, but by then he was steering Russia’s course.
The events of 2014 did alarm me – Putin’s plans for a gradual takeover of Ukraine, foiled by US-supported demonstrations in Kyiv’s Maiden Square, followed by Russia’ stealth repossession of the Crimean peninsula. In 2016, expecting that Clinton would be elected, I began writing Because They Could: The Harvard-Russia Scandal (And NATO Expansion) after Twenty-five Years (Create Space, 2018)
Instead Donald Trump was elected. His longstanding relationship with Russian government and various Russians put the matter on hold. Joe Biden defeated Trump four years later and the momentum of NATO expansion was seamlessly reasserted, notably with signing on Nov. 10, 2021 of a U.S.-Ukraine Charter of Strategic Partnership. Barely three months later, Putin attempted his ill-fated blitzkrieg. The subsequent invasion was mostly turned back, except in the eastern Donbass region.
What’s done is done. The issue seems to me to have been decided, mostly by the citizens and soldiers of Ukraine. The U.S. may or may not bear responsibility for having fomented the war by pressing the boundaries – and the culture – of NATO ever closer to Russia, but having reached this point in Putin’s war on Ukraine, America has no honorable alternative but to stay the course until Putin stands down. He will do so only after more defeats on the battlefield; after taking account of the devastation he has caused, no less to his own country than to Ukraine; and to Russia’s reputation forever. His pursuit of restoration of Russian status as a superpower was a pipedream.
What is next? Partition is apparently what the Pentagon expects, once Russia’s spring offensive grinds to a halt. That makes sense to me. Russia gets to keep portions of Eastern Ukraine that it already possesses. Ukraine retains what it has already recaptured; remains independent; and gradually becomes a member of NATO and the European Union.
In the meantime, continued support for Ukraine is about to become a matter of partisan politics in the 2024 presidential election campaign. So much the better: it will be one more litmus test with which to separate the real Republican Party from Trumplican rear-guard. The war in Ukraine offers an opportunity to begin to put US politics together again.
It is time to begin to gather assessments of America’s behavior in world affairs during the last thirty years. Historian M. E. Sarotte has made an especially good start with her most recent book, Not One Inch: America, Russia, and the Making of Post- Cold War Stalemate (Yale, 2021), but, as she notes, her account covers only the beginning; it ends in 1999. Her next volume presumably will cover the years to 2016. By that time, today’s war will be over, and the saga of the post- Cold War world ripe for a third volume.
Frank Costigliola’s biography Kennan: A Life between Two Worlds (Princeton, 2023) adds some details to the story of diplomat George Kennan’s famous op-ed piece opposing NATO expansion, “A Fateful Error,” in The New York Times, in 1996, but we will have to wait some time for a dispassionate biography of Strobe Talbott, President Clinton’s old Oxford friend, the architect of NATO expansion. Newspaper journalists, Peter Baker of The Times foremost among them, can be expected to begin to illuminate some shadows.
The change of heart about the war that I’m describing – putting aside for now the idea of joint responsibility in favor of rendering sufficient support to Ukraine, whatever it costs, until independence and peace are won – has been a long and painful time in coming. America has not done well in its three major wars in my adulthood – Vietnam, Afghanistan, and Iraq. In Ukraine, it finally seems vital to stay the course.
xxx
I caught a windjammer of a cold over the holidays and failed to post to EcononomicPrincipals.com in timely fashion what he had written before the storm. He put it up when calm returned. Apologies to those accustomed to reading it there.
More to the point, all good wishes to readers for the coming year.
David Warsh, a veteran columnist and an economic historian, is proprietor of Somerville-based economicprincipals.com, where this column originated.
‘A certain impermanence’
“The Needle’s Mark and Maquoketa” (quilt fragments, gesso, acrylic), by Susan Denniston, in her show “Voices Carry,’’ at Kingston Gallery, Boston, Jan. 5-29. She lives near the ocean south of Boston.
The gallery says:
“When artists work with materials created and shaped by previous generations, it evokes memories and pulls a thread from the past through the present and into the future. Working with inherited, delicate cloth, Denniston listens and acknowledges our fragility, our vulnerability, and our certain impermanence.’’
Read more.
‘Deeper in’
“Sumac thickets by the roadbed, either side,
spangled by snow and the big moon’s light.
Deeper in, evergreens, taller, darker,
but still undark in that light, this weather.’’
— From “Inviting the Moose: A Vision,’’ by Sydney Lea (born 1942), a former poet laureate of Vermont who has taught at various New England colleges.
Adjust your attitude
“Better Times” (mixed media), by Susan Leskin, in the group members show at Galatea Fine Art, Boston, Jan. 13-29.
"It feels important right now to find and express visions of hope and lightness to counter the despair that many of us feel about the current state of the world. These collages reflect those visions for me."
Her artist statement says:
“My work frequently explores connectivity and disjunction. I enjoy creating images that are ambiguous and may be just on the edge of recognition. There is often a focus - explicit or implied - on the relationship between humans and nature.
”I use fluid acrylic paint and mediums, ink, pencil, and painted papers in my collages.’’
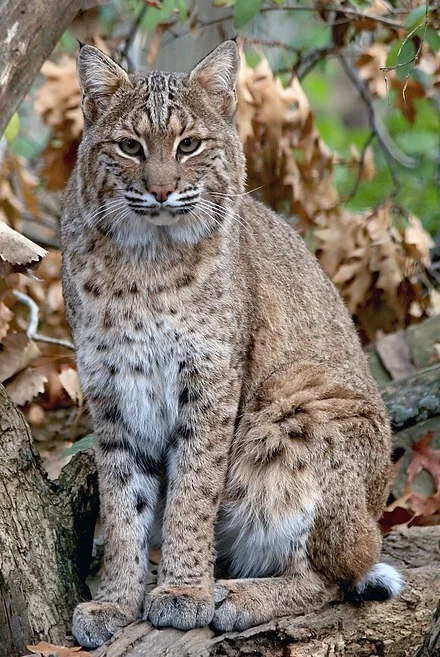
Bonnie Phillips: Those secretive and opportunistic Bobcats
Bobcat
Text from ecoRI News (ecori.org)
JOHNSTON, R.I.
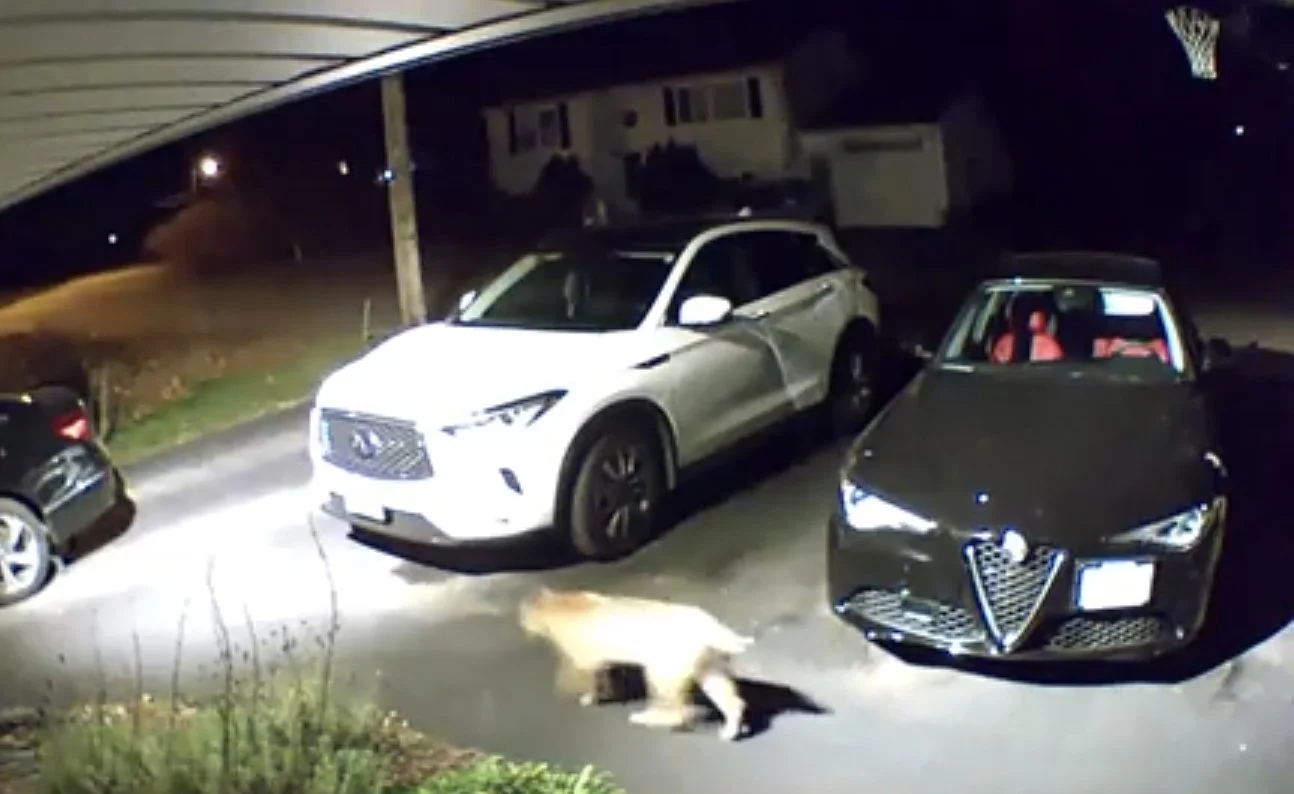
The big cat saunters across the driveway, bobbed tail swaying, passing in front of two parked cars before the doorbell camera cuts off.
The video, posted on the neighborhood app Nextdoor, came with a question: Anyone else see an animal like this? It looks like a bobcat.
After watching the video, Mary Gannon, the wildlife outreach coordinator for the Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management’s Division of Fish and Wildlife, confirmed the animal is “a very healthy-looking Bobcat.”
Is it unusual for a Bobcat to be wandering around suburban Johnston? Not so much, said Morgan Lucot, a furbearer biologist with DEM. Bobcats are “very adaptable,” and are the most widely distributed feline in North American, she said.
Bobcats are “meso-carnivores,” meaning they will eat just about any animal, from squirrels to birds to snakes to small deer, according to Lucot.
It’s undetermined how many Bobcats roam Rhode Island, Lucot said, but their numbers are growing. Although the habitats they prefer — forested land, large fields — are diminishing, their adaptability means they can adjust to any environment.
A Bobcat was captured on a doorbell camera walking across a driveway in Johnston, R.I.
— Photo from Nextdoor
“Carnivores that are highly adaptable aren’t always negatively affected by” an urban environment, Lucot said, and can sometimes turn it to their advantage, eating backyard chickens, say, or unsecured trash.
“We’ve gotten sightings from Johnston before, as well as from Smithfield and Cranston,” Gannon said. Although Bobcats can be found throughout Rhode Island, their highest numbers are in Washington County.
Bobcat kittens
The shy, secretive cats are solitary, unless they are mating or raising young. The cats mate between February and May, and the kittens — an average litter has three — are born in June. The young stay with the mother until the following spring. Lucot said while she’s rearing her kittens the mother will choose a den, usually in a boulder pile or underneath exposed tree roots. She said she’s known Bobcats to den under a shed, near a plentiful supply of food.
Bobcats are roamers, Lucot said, walking up to 12 miles a night. The cats are crepuscular, meaning they are most active at dawn and dusk. DEM partnered with the University of Rhode Island several years ago to track Bobcats with GPS collars, Gannon said. A video discussing the results of the study can be found on YouTube. One Bobcat tagged in the study was tracked from South Kingstown to eastern Connecticut and back over the course of a week.
Bobcats are native to New England and were considered “varmints” by early settlers and were hunted as such. It wasn’t until 1969 that Massachusetts, the first New England state to do so, declared the Bobcat a “game species,” which meant the cats could only be hunted during a particular time, and there was a limit to how many could be killed.
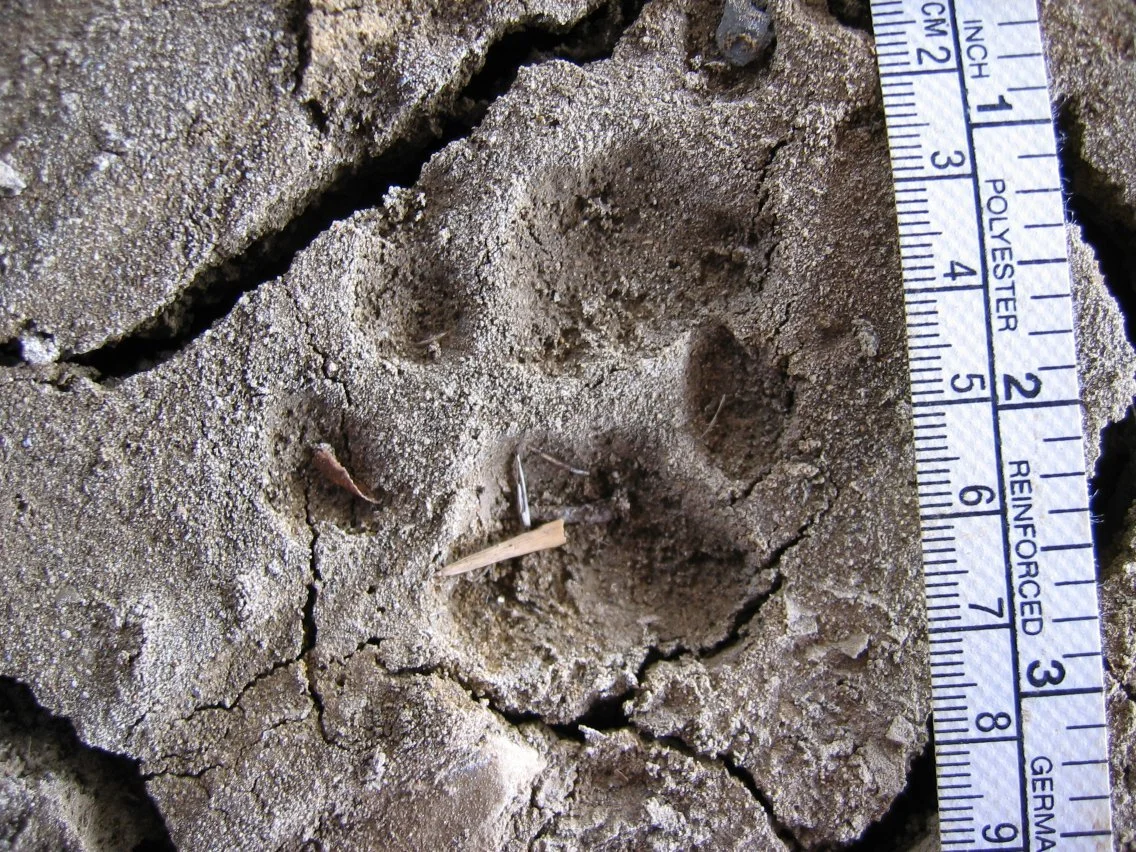
The difference between dog and cat tracks. (State of Michigan)
So what should you do if you suspect you are sharing your land with a bobcat? First, look for tracks. Bobcat tracks look like common house cats’, only much larger: Bobcat tracks are typically about 1 1/2 inches long by 1 3/8 inches wide. In contrast, coyote (and most other dog tracks) are longer than they are wide. Bobcats weigh between 15 and 30 pounds, and with their fluffy fur can look much larger.
“They look like cute furry cats but are not,” Lucot warned. Don’t approach them, she said. Instead, make noise, bang pots and pans, and “shoo them away.”
“It’s best for the animal to be scared,” Lucot said. “We don’t want them getting used to people.”
While “it might be exciting to get a Bobcat in our backyard, it’s not legal to feed them,” Lucot said.
She recommended that homeowners bring in small animals and livestock, such as chickens, after dark. Enclosures should be checked frequently for holes, and outdoor pet dishes should be brought in overnight as well.
Bonnie Phillips is a journalist with ecoRI News.
Bobcat tracks in mud showing the hind-paw print (top) partially covering the fore-paw print (center)
— Photo by Lensim
Grownup state
“Massachusetts is the first state in America to reach full adulthood. The rest of America is still in adolescence.”-
— Uwe Reinhardt 1937-2017), health-care economist
Llewellyn King: U.S. airlines gouge and pack
WEST WARWICK, R.I.
A Conservative British Prime Minister, Edward Heath, coined the phrase “the unacceptable face of capitalism” in 1973. He was describing the actions of Roland Walter “Tiny” Rowland and the company he headed, Lonrho (London Rhodesia), a mining and real-estate conglomerate with interests across Africa.
Having had a hectic travel schedule since the end of the COVID-19 lockdown, I can say that the airlines have become an unacceptable face of capitalism.
I refer to the airlines collectively because from the traveling public’s point of view, they are a massive whole with little to choose between them. Nominally in competition, their attitude to the public has become a common one of disrespect.
That one of the airlines, Southwest, would implode when stressed was no surprise. A metamorphosis had taken place in the last two years with the passengers -- the customers – becoming, in the collective airline psyche, just economic opportunities, ripe for endless upselling.
When the airlines realized that they could extract money over and above the ticket price, they began a service free fall and abandoned any pretense of respect for their customers -- or, apparently, themselves. They, the customers, had become economic targets for exploitation.
First came the baggage charges. Surely, the airlines knew people didn’t travel without bags and could have allowed for that in ticket pricing.
Then they found they could upsell the seating, making passengers pay extra for marginally better seats, and even for boarding about five minutes early.
On a recent flight in a Boeing 767, the airline was charging a stiff premium to sit in the double seats near the window rather than in the three abreast in the middle. My wife and I stayed in the middle.
A new class of service called “basic economy” has prohibited carry-ons in the overhead bins, forcing passengers to pay for checked baggage and wiping out some of their flight-cost savings.
I have flown round the globe for decades and have known every class of service, from that on the Concorde to the wonders of first class on Asian air carriers. But mostly, I have sat in the back and watched as the aircraft have gotten older and shabbier, as the seating area has shrunken, as the lavatories have shrunken in number and size, as the snacks and food offering are as incomprehensible as they are inedible, and as the flexibility of tickets has disappeared.
In tandem with these deteriorations in comfort, service and pricing, has come cancellation of normal business practices when it comes to cash and credit cards. You can no longer buy a ticket with cash at the airport. You can’t use a credit card on board for a snack if you haven’t pre-registered your credit card and, in many cases, you must have your own device to watch entertainment.
For a fee, of course, you can now get Wi-Fi on many airlines. But the seats are so positioned that you can’t, in my experience, open a laptop and work. For another fee, they may have a fix.
As I have strapped myself into a sometimes-broken seat (which reclines about 2 inches), looking at the ashtray (which indicates the age of the cabin furnishings), I have begun to wonder to what extent this predatory approach to passengers, this total indifference to those who pay the stiff fares and all the fees on top, has filtered down to the maintenance department.
Passengers, I guess, are inured to the horrors of airline travel and the victimhood that goes with it. Know this: If you are trying to travel by air, you have identified yourself as an economic target for a group of companies, the airlines, which supposedly compete but which, within hours, match every new fee dreamed up by one of their supposed competitors.
The latest serious inequity is defrauding passengers by reducing the value of their frequent-flyer miles.
U.S. Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg needs to take a root-and-branch look at the airlines: the greed, the collusion and the manifest disrespect for the passengers that is pervasive. Importantly, he needs to look at seat size and aisle width and their impact on safety.
I have a full flying schedule ahead in January, and I am preparing for my time in the gouging skies with trepidation and resignation.
Llewellyn King is executive producer and host of White House Chronicle, on PBS. He’s based in Rhode Island and Washington, D.C.
On Twitter: @llewellynking2
Where abnormal is normal
1816 was called “The Year Without a Summer” in New England because of the effects of a huge volcanic eruption in Indonesia, which blocked much of the sun’s heating power on Earth. Hannah Dawes Newcomb, of Keene, N.H., kept a diary (above) with short daily reports on her everyday life. Starting around May, her comments reflected the strange weather patterns of that year, which were disastrous for agriculture in North America, Europe and elsewhere.
“Freak weather conditions are standard in New England. In fact, The Old Farmer’s Almanac was vaulted on the road of success by predicting “snow and ice” for July 13, 1816. When it actually did snow on Boston that day, most of Robert B. Thomas’s 1,500 competitors faded into oblivion.’’
—Judson D. Hale, now former editor of Yankee magazine and The Old Farmer’s Almanac, writing in Arthur Griffin’s New England: The Four Seasons (1980).
Expand and contract
“Edge of Snow” (acrylic and photo on paper), by Cape Cod-based Jane Lincoln, at Kingston Gallery, Boston.
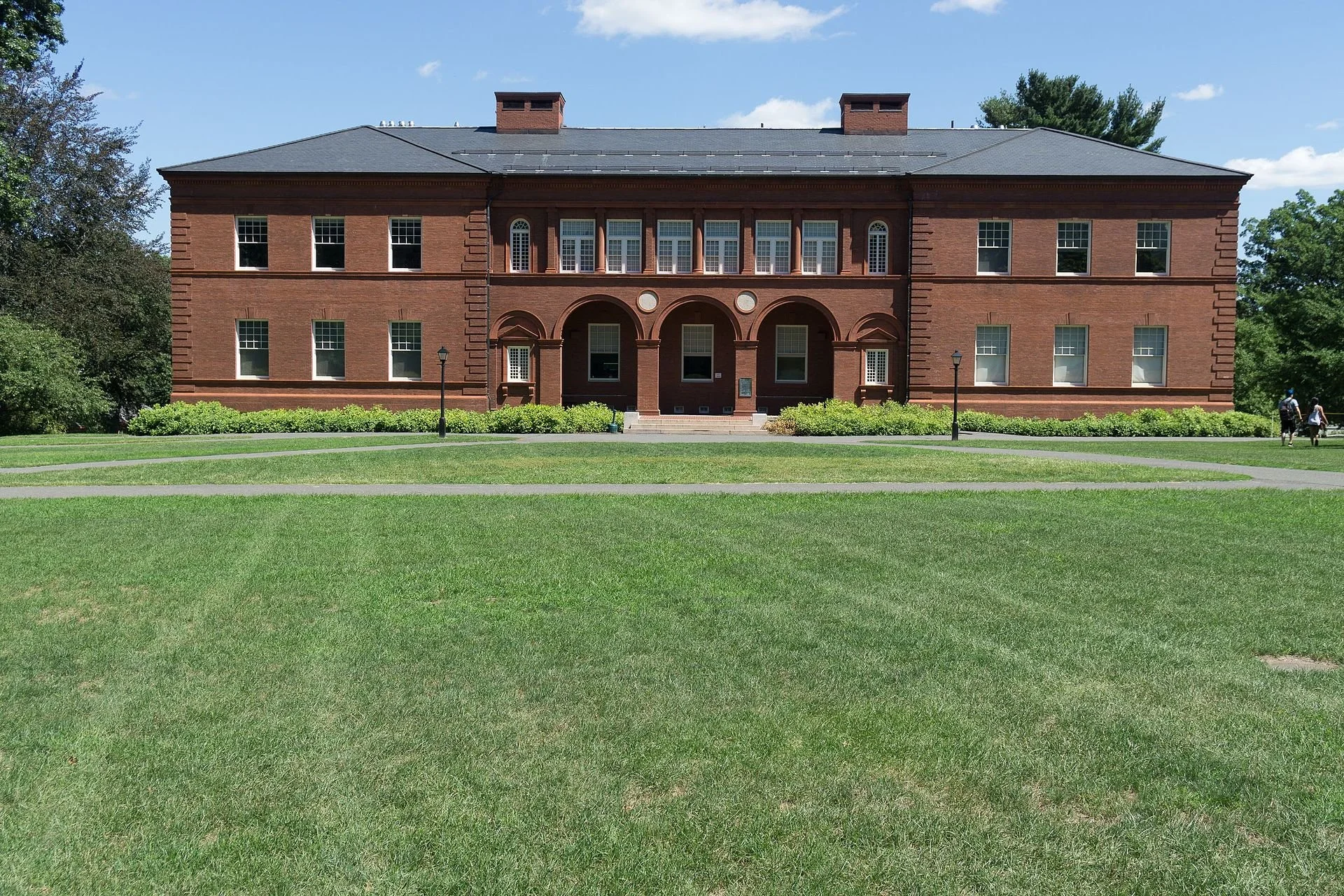
A baby Hercules of a college
Fayerweather Hall at Amherst College. Founded in 1821, the college, in Amherst, Mass., developed from Amherst Academy, first established as a secondary school. The college was originally suggested as an institution to succeed Williams College (founded in 1793), in Williamstown, Mass., which was struggling to stay open but later thrived. The two rather similar elite colleges remain friendly rivals.
“The infant {Amherst} college is an Infant Hercules. Never was so much striving, outstretching, & advancing in a literary cause as is exhibited here.’’
— Ralph Waldo Emerson (1823)
Founded in 1821, Amherst College, in Amherst, Mass., developed from Amherst Academy, first established as a secondary school. The college was originally suggested to succeedWilliams College, in Williamstown, Mass., which was struggling to stay open but later thrived.
xxx
“You can always tell a Harvard man, but you can’t tell him much.’’
— Anonymous
The joy and pain of shrinkage
Big enough
— Photo by Cavajunky
From Robert Whitcomb’s “Digital Diary,’’ in GoLocal24.com
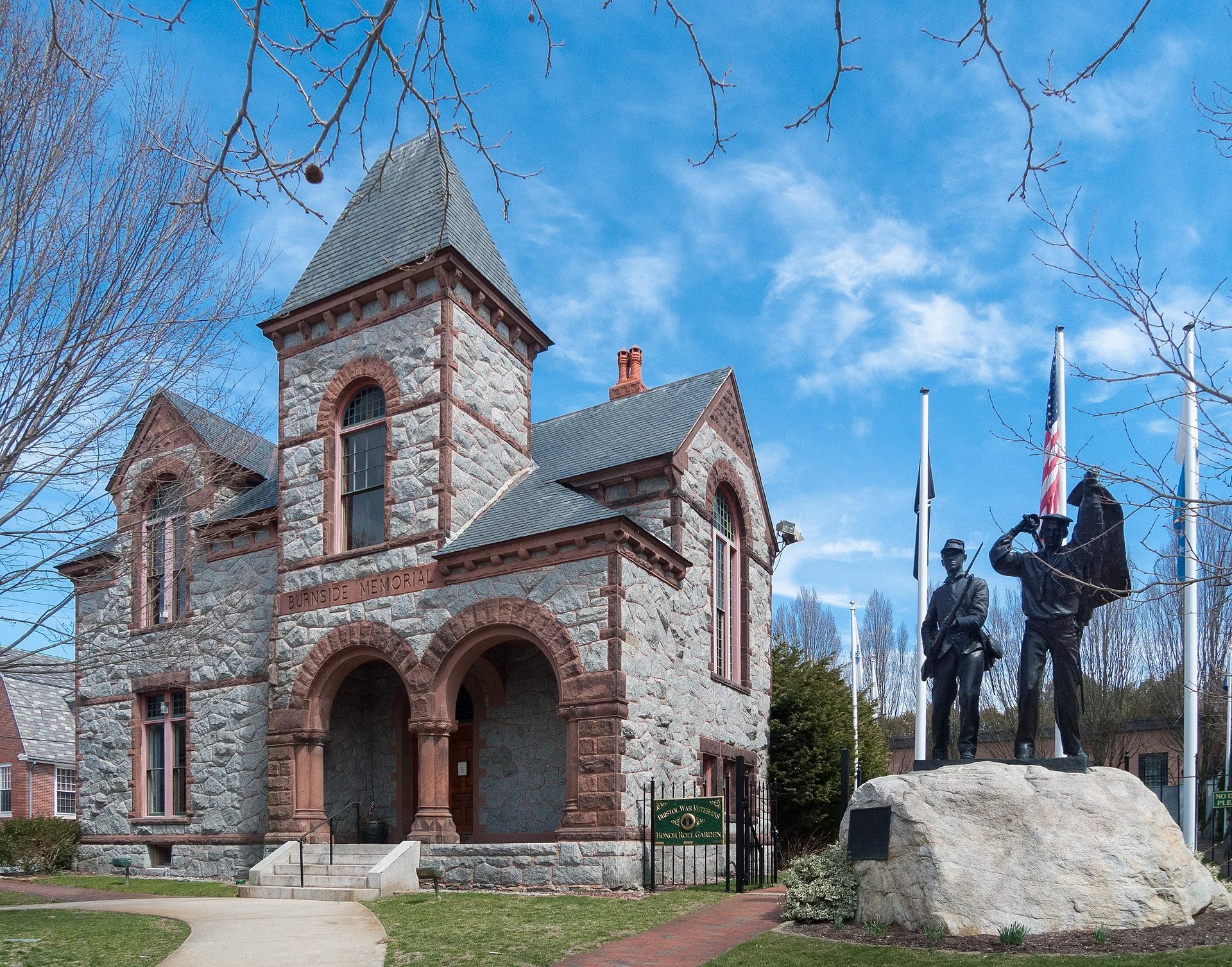
Many people at the end of the year reflect on whether they should make a major life change. This might include simplifying by downsizing where they live.
So I recommend Dr. Edward Iannuccilli’s latest book of essays, Essays on the Art and Pain of Downsizing. (He’s a friend, but no, I get no kickbacks for this plug.)
Of course, many older people, such as Dr. Iannuccilli, who lives in beautiful Bristol, R.I., downsize in part because of their stage of life. But there are good reasons for others to do so. You save on fuel, electricity, taxes and insurance and you’re disciplined to get rid of stuff, which can feel liberating. (Do some people have so much stuff that it acts as insulation, saving fuel in the winter?)
In 1980, the median size of a new house in the U.S. was 1,595 square feet. That ballooned to 2,386 square feet by 2018, with fewer people living in these houses. Obviously, the bigger the house, the bigger the purchase price and maintenance costs; the latter tend to be alarmingly unpredictable.
Town hall and Civil War memorial in Bristol, R.I.
Individual terror
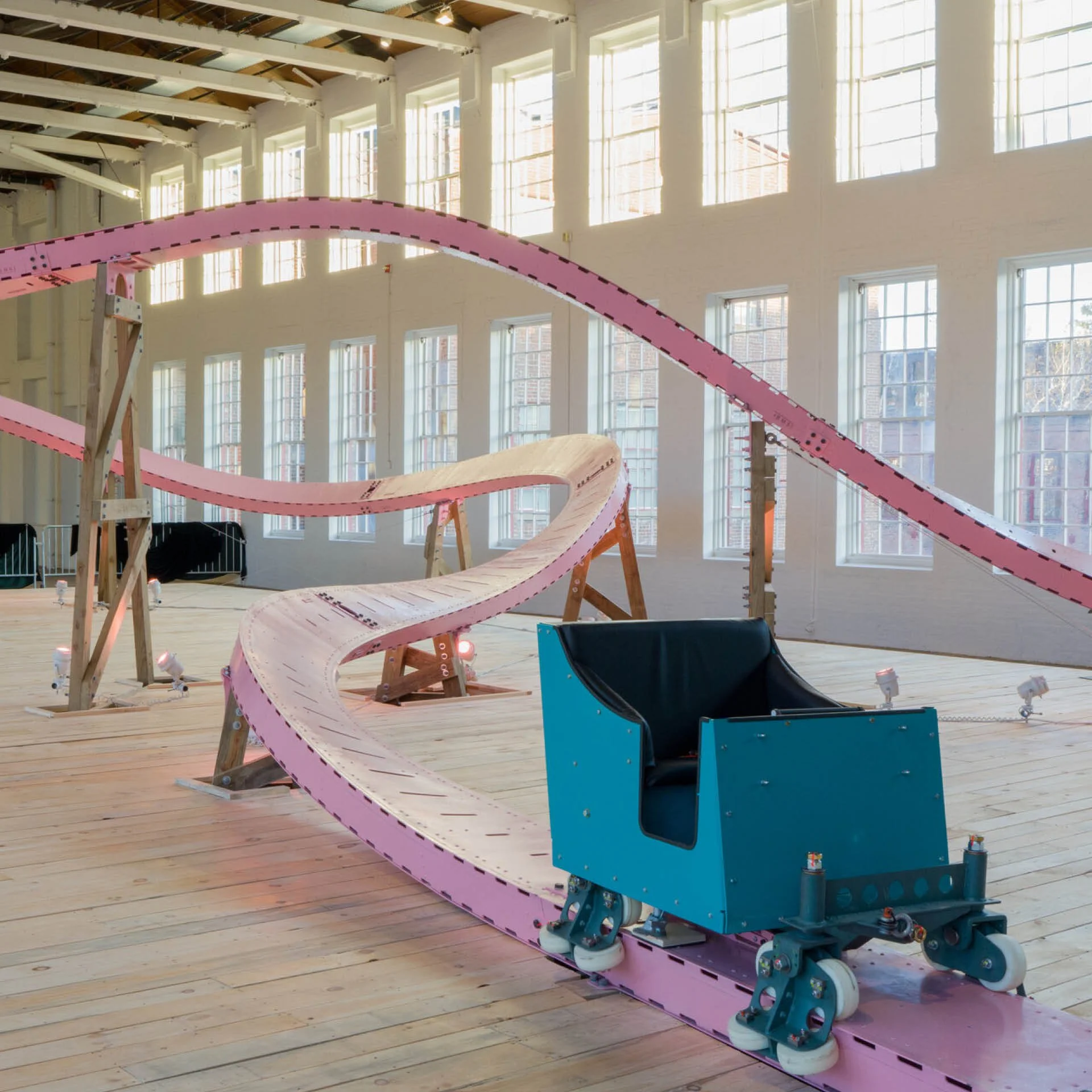
“Brake Run Helix,’’ by EJ Hill, at the Massachusetts Museum of Contemporary Art (MassMOCA), North Adams., Mass., through January 2024.
The museum explains:
“In ‘Brake Run Helix,’ Hill inverts the experience of riding a roller coaster, transforming it from a shared ritual of joy and terror to an individual performance: only one person may ride the roller coaster, Brava!, at a time. Brava!’s single cart emerges from behind a two-story velvet stage curtain, moves across the coaster’s pink tracks, and ultimately comes to rest on the wooden stage, while onlookers observe from below. Visitors can see the roller coaster activated by riders throughout the day. Are you interested in riding? The line starts here.’’
French-Canadians at New Year's
L'Église du Précieux Sang (also known as The Church of the Precious Blood) has served the large French-Canadian population of Woonsocket, R.I., area since the 1870’s.
The Fleur de Lis, the symbol of French Canada.
From a New England Historical Society article on French Canadians in New England:
“The reveillon is a long, late dinner preceding a holiday. Tourtiere is central to the meal. The celebrated meat pie, cooked and eaten during the shortest days of winter, often accompanies traditional Franco-American foods such as peas or pea soup, head cheese, croquignoles and ragout.
“During the first half of the 19th century, when the first wave of immigrants arrived, New Year’s Day exceeded Christmas in importance. On January 1, Franco-Americans exchanged small gifts, and children found presents under the tree or near the manger in the parlor. Sometimes their parents told them the presents came from le Pere Noel (a skinny version of Santa Claus) or l’Enfant Jesus.’’
Chris Powell: Housing with steeples; report on where you are
— Photo by Andrea Farias
MANCHESTER, Conn.
With an extension of one of his epidemic-related emergency orders, Connecticut Gov. Ned Lamont has saved for another six months the Pacific House homeless shelter in Danbury, just days before it would have had to close because of the expiration of his previous order and the city zoning board's disgraceful refusal to approve the facility.
Thus Connecticut has just barely avoided being shamed by the expulsion of dozens of people into the dead of winter during Christmas week, what would have been a grotesque re-enactment of there being “no room at the inn” as there famously was no room two millennia ago.
But of course the shame may be only postponed. While in the last few years state government sharply reduced homelessness, in recent months it has been rising again as the economy has weakened, inflation has soared, and the poorest and most troubled and demoralized have been most battered.
Getting them out of the cold and into a safe, secure and warm environment with access to medical care and encouragement is again an urgent obligation for state government, even as practically every day state government touts its comfortable financial condition and bestows money on far less compelling projects.
With the new session of the General Assembly convening in a few days, the governor's extended order preserving the Danbury shelter should be only the start of an emergency program to establish more shelters and supportive housing facilities throughout the state and to exempt them from municipal zoning regulations.
With organized religion declining, Connecticut abounds in empty church buildings, some of which are being offered for sale and repurposing, even if repurposing a building with a steeple may create a permanent incongruity for the new occupants.
Organized religion's decline is not just a decline in theology and doctrine but also a decline in community, which can be seen in the worsening social disintegration generally. While in the old days religion could be politically divisive, in recent years in Connecticut it has stressed decency more than doctrine and so should be much missed.
In pursuit of that decency maybe state government should lease some of those former churches for use as shelters and supportive housing, and maybe the neighbors, in danger of being rebuked by the antique architecture for any lack of hospitality, would'’t object.
xxx
A congressional district on Long Island that includes parts of the New York City borough of Queens and neighboring Nassau County on Nov. 8 elected Republican George Santos to Congress. His resume, the New York Times reported last week, is completely phony.
The representative-elect turns out not to be what he claimed during his campaign -- a great scholar with a brilliant record in the financial industry -- but a grifter who fled criminal prosecution in Brazil and has been evicted from apartments in New York for not paying rent.
Of course he should resign his office, and if he refuses, the House of Representatives should expel him. There should be a new election in his district. But even then the country should expect a lot more of this fraud, for it is the consequence of the decline of journalism, which in turn is a consequence of the decline of literacy and civic engagement throughout the country.
After all, creditable as the Times' exposure of the grifter is, where were the newspaper and other news organizations purporting to serve Queens and Nassau County before his election?
Of course The Times was tediously savaging Donald Trump long after his presidential term had ended, just as most major news organizations were doing. But The Times declines to cover its own neighborhood seriously.
Connecticut has no cause to snicker here. While all the members of the state's congressional delegation who were just re-elected have had long careers in public life and have been fully vetted, as Governor Lamont, also just re-elected, has been, the three new state constitutional officers remain almost completely unknown, and the backgrounds of many new state legislators just elected have not been scrutinized independently by vigorous journalism. For there isn't much left.
The new constitutional officers and state legislators may turn out all right. But there is no longer much insurance anywhere against disasters like the one in New York.
Chris Powell (CPowell@JournalInquirer.com) is a columnist for the Journal Inquirer, in Manchester.
Blue: ‘Strength and calm’
“Blue Silence” (acrylic on canvas), by Reading, Mass.-based painter Jo-Anne Boback, in the group show “Looking Forward,’’ at Galatea Fine Art, Boston, Jan. 13-29.
She explains:
"I did this piece after I lost my dad, who had the deepest blue eyes! As it is with most of us, the color blue represents calm while evoking strength, stability and security; think of the ocean and the sky."
Downtown Reading.
The Parker Tavern, built in 1694, is the oldest surviving building in Reading. It was owned and operated by Ephraim Parker, who was the great-grandson of Thomas Parker, who was one of Reading’s founders and probably named the town, after Reading, England. The tavern is now a museum.
Samantha Young: Poorly trained, politically connected coroners
“Autopsy” (1890), by Enrique Simonet
“There are some really egregious conflicts of interest that can arise with coroners.’’
— Justin Feldman, a visiting professor at Harvard University’s FXB Center for Health and Human Rights
When a group of physicians gathered in Washington state for an annual meeting, one made a startling revelation: If you ever want to know when, how — and where — to kill someone, I can tell you, and you’ll get away with it. No problem.
That’s because the expertise and availability of coroners, who determine cause of death in criminal and unexplained cases, vary widely across Washington, as they do in many other parts of the country.
“A coroner doesn’t have to ever have taken a science class in their life,” said Nancy Belcher, chief executive officer of the King County Medical Society, the group that met that day.
Her colleague’s startling comment launched her on a four-year journey to improve the state’s archaic death-investigation system, she said. “These are the people that go in, look at a homicide scene or death, and say whether there needs to be an autopsy. They’re the ultimate decision-maker,” Belcher added.
Each state has its own laws governing the investigation of violent and unexplained deaths, and most delegate the task to cities, counties, and regional districts. The job can be held by an elected coroner as young as 18 or a highly trained physician appointed as medical examiner. Some death investigators work for elected sheriffs who try to avoid controversy or owe political favors. Others own funeral homes and direct bodies to their private businesses.
Overall, it’s a disjointed and chronically underfunded system — with more than 2,000 offices across the country that determine the cause of death in about 600,000 cases a year.
“There are some really egregious conflicts of interest that can arise with coroners,” said Justin Feldman, a visiting professor at Harvard University’s FXB Center for Health and Human Rights.
Belcher’s crusade succeeded in changing some aspects of Washington’s coroner system when state lawmakers approved a new law last year, but efforts to reform death investigations in California, Georgia and Illinois have recently failed.
Rulings on causes of death are often not cut-and-dried and can be controversial, especially in police-involved deaths such as the 2020 killing of George Floyd. In that case, Minnesota’s Hennepin County medical examiner ruled Floyd’s death a homicide but indicated a heart condition and the presence of fentanyl in his system may have been factors. Pathologists hired by Floyd’s family said he died from lack of oxygen when a police officer kneeled on his neck and back.
In a recent California case, the Sacramento County coroner’s office ruled that Lori McClintock, the wife of Congressman Tom McClintock, died from dehydration and gastroenteritis in December 2021 after ingesting white mulberry leaf, a plant not considered toxic to humans. The ruling triggered questions by scientists, doctors and pathologists about the decision to link the plant to her cause of death. When asked to explain how he made the connection, Dr. Jason Tovar, the chief forensic pathologist who reports to the coroner, said he reviewed literature about the plant online using WebMD and Verywell Health.
The plant is generally considered safe and is used as an herbal remedy for a variety of ailments. Her death highlights the potential dangers of dietary supplements.
The various titles used by death investigators don’t distinguish the discrepancies in their credentials. Some communities rely on coroners, who may be elected or appointed to their offices, and may — or may not — have medical training. Medical examiners, on the other hand, are typically doctors who have completed residencies in forensic pathology.
In 2009, the National Research Council recommended that states replace coroners with medical examiners, describing a system “in need of significant improvement.”
Massachusetts was the first state to replace coroners with medical examiners statewide, in 1877. As of 2019, 22 states and the District of Columbia had only medical examiners, 14 states had only coroners, and 14 had a mix, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The movement to convert the rest of the country’s death investigators from coroners to medical examiners is waning, a casualty of coroners’ political might in their communities and the additional costs needed to pay for medical examiners’ expertise.
The push is now to better train coroners and give them greater independence from other government agencies.
“When you try to remove them, you run into a political wall,” said Dr. Jeffrey Jentzen, a former medical examiner for the city of Milwaukee and the author of “Death Investigation in America: Coroners, Medical Examiners, and the Pursuit of Medical Certainty.”
“You can’t kill them, so you have to help train them,” he added.
There wouldn’t be enough medical examiners to meet demand anyway, in part because of the time and expense it takes to become trained after medical school, said Dr. Kathryn Pinneri, president of the National Association of Medical Examiners. She estimates there are about 750 full-time pathologists nationwide and about 80 job openings. About 40 forensic pathologists are certified in an average year, she said.
“There’s a huge shortage,” Pinneri said. “People talk about abolishing the coroner system, but it’s really not feasible. I think we need to train coroners. That’s what will improve the system.”
Her association has called for coroners and medical examiners to function independently, without ties to other government or law enforcement agencies. A 2011 survey by the group found that 82 percent of the forensic pathologists who responded had faced pressure from politicians or the deceased person’s relatives to change the reported cause or manner of death in a case.
Dr. Bennet Omalu, a former chief forensic pathologist in California, resigned five years ago over what he described as interference by the San Joaquin County sheriff to protect law enforcement officers.
“California has the most backward system in death investigation, is the most backward in forensic science and in forensic medicine,” Omalu testified before the state Senate Governance and Finance Committee in 2018.
San Joaquin County has since separated its coroner duties from the sheriff’s office.
The Golden State is one of three states that allow sheriffs to also serve as coroners, and all but 10 of California’s 58 counties combine the offices. Legislative efforts to separate them have failed at least twice, most recently this year.
AB 1608, spearheaded by state Assembly member Mike Gipson (D-Carson), cleared that chamber but failed to get enough votes in the Senate.
“We thought we had a modest proposal. That it was a first step,” said Robert Collins, who advocated for the bill and whose 30-year-old stepson, Angelo Quinto, died after being restrained by Antioch police in December 2020.
The Contra Costa County coroner’s office, part of the sheriff’s department, blamed Quinto’s death on “excited delirium,” a controversial finding sometimes used to explain deaths in police custody. The finding has been rejected by the American Medical Association and the World Health Organization.
Lawmakers “didn’t want their names behind something that will get the sheriffs against them,” Collins said. “Just having that opposition is enough to scare a lot of politicians.”
The influential California State Sheriffs’ Association and the California State Coroners Association opposed the bill, describing the “massive costs” to set up stand-alone coroner offices.
Many Illinois counties also said they would shoulder a financial burden under similar legislation introduced last year by state Rep. Maurice West, a Democrat. His more sweeping bill would have replaced coroners with medical examiners.
Rural counties, in particular, complained about their tight budgets and killed his bill before it got a committee hearing, he said.
“When something like this affects rural areas, if they push back a little bit, we just stop,” West said.
Proponents of overhauling the system in Washington state — where in small, rural counties, the local prosecutor doubles as the coroner — faced similar hurdles.
The King County Medical Society, which wrote the legislation to divorce the two, said the system created a conflict of interest. But small counties worried they didn’t have the money to hire a coroner.
So, lawmakers struck a deal with the counties to allow them to pool their resources and hire shared contract coroners in exchange for ending the dual role for prosecutors by 2025. The bill, HB 1326, signed last year by Democratic Gov. Jay Inslee, also requires more rigorous training for coroners and medical examiners.
“We had some hostile people that we talked to that really just felt that we were gunning for them, and we absolutely were not,” Belcher said. “We were just trying to figure out a system that I think anybody would agree needed to be overhauled.”
Samantha Young is a Kaiser Health News reporter.
Samantha Young: syoung@kff.org, @youngsamantha
Visit in a storm
At the Cape Cod National Seashore.
“What are springs and waterfalls? Here is the spring of springs, the waterfall of waterfalls. A storm in the fall or winter is the time to visit it; a light-house or a fisherman's hut the true hotel. A man may stand there and put all America behind him.’’
— Henry David Thoreau (1817-1862), in Cape Cod
Provincetown in Thoreau’s lifetime.
Don Pesci: What is a woman?
Detail from Johannes Vermeer’s (1632-1675) “Portrait of a Woman With a Pearl Earring’’
VERNON
The absurdities of post-modern life press upon us like some finely tuned, automatically updated incubus.
Awaiting approval for her nomination to be on the U.S. Supreme Court, current Associate Supreme Court Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson was asked, by a woman legislator, as it happened, to “define a woman.”
She demurred, modestly pleading that she was no biological scientist.
But the question, not entirely innocently presented, begs to be answered. When I put the question to two politically unbiased women, both agreed that a “woman” may be defined as one who receives flowers from a male admirer.
I cannot remember ever having received a bouquet of flowers from a woman. I have given out a few bouquets of flowers to women I admire and cannot recall ever having sent a bouquet to a man.
So far, so good.
Naturally, there are exceptions, but exceptions generally prove the rule, except in rare cases when it becomes politically expedient to make a rule of an exception. This nearly always ends in disaster. Both rules and definitions should be generally accepted by what the ordinary run of humanity would regard as objective and dispassionate observers.
My grandfather – Carlo “The Fox” – stands out as an exception … sort of.
One day, when I was storming through my reckless teens, “The Old Man,” as everyone affectionately called Grandfather Carlo, showed up at the Pesci homestead clutching a fist full of Bennies, which he pressed upon his daughter Rose, my mother.
This took her, the immediate family, the extended family and, for all I know, any relatives in Italy who knew Carlo well, by surprise. Carlo The Fox was abstemious when it came to money, not exactly a Scrooge, but close.
“What’s this for?” my mother asked.
Sitting by the kitchen window, the early morning sun bathing his weather ravaged face, he explain that he was old.
My mother nodded assent, a question mark mysteriously appearing on her forehead.
He sipped his “coffee royal” -- steaming hot black coffee, just short of an espresso, never to be diluted with anisette -- while his daughter waited patiently for him to explain why on this day he had abandoned a lifetime of penny-pinching. To be sure, he had in the past made rare exceptions to his inflexible habit, most often when he was engaged in card games for money, not sport. In one game, he had won, and then lost a portion of Elm Street in Windsor Locks, Conn.
My mother groaned when she discovered this. “We could have been rich,” she observed.
Rose waited him out. And, sipping his coffee, to which was added a knuckle of Jack Daniels, it came bubbling out of him like a freshet of living water.
He did not expect to live too many years longer, most of his friends were dead, he could not – dare not! – trust anyone with the mission he assigned my mother. When he died – unfortunately the fate of all men, rich, poor and moderately well-off – she was to take the money and with it buy flowers for his wake and funeral. He did not want to go out un-flowered or unrespected by the few of his friends who might survive him.
My mother, who had gotten used to her father’s abstemiousness -- though he had made an exception in the case of coffee-royals and Italico Classico Ammezzato cigars, a refined blend of Italian and Kentucky, he was pleased to note -- was touched and instantly accepted the commission. When Carlo The Fox died, his body was smothered in flowers.
So here was a woman buying flowers for a man – to be sure, with the man’s money – an exception that proves the rule.
Few of us are linguistic scientists or professors of grammar, morphology, syntax, phonology, phonetics, and semantics. We are not Noam Chomsky, a reliable guide when he does not meander outside his discipline. The definition of a woman as “one who receives flowers from an admiring gentleman” is serviceable and practical, allowing for arcane exceptions that, given the postmodern bad habit of redefining foundational characteristics, does not touch embarrassing and painful questions such as “Should elementary school libraries stock Gender Queer and Lawn Boy?”
Don Pesci is a Vernon-based columnist.
Toll bridge over the Connecticut River, c. 1910.